Form validation for newbies to PHP
PHP Form Validation
We need to consider security when processing PHP forms.
In this chapter we will demonstrate the secure processing of PHP form data. In order to prevent hackers and spam, we need to perform data security verification on the form
Next we will look at the following examples of form verification:
<!DOCTYPE HTML>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>php中文網(wǎng)</title>
<style>
.error {color: #FF0000;}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<?php
// 定義變量并默認(rèn)設(shè)置為空值
$nameErr = $emailErr = $genderErr = $websiteErr = "";
$name = $email = $gender = $comment = $website = "";
if ($_SERVER["REQUEST_METHOD"] == "POST")
{
if (empty($_POST["name"]))
{
$nameErr = "名字是必需的";
}
else
{
$name = test_input($_POST["name"]);
// 檢測名字是否只包含字母跟空格
if (!preg_match("/^[a-zA-Z ]*$/",$name))
{
$nameErr = "只允許字母和空格";
}
}
if (empty($_POST["email"]))
{
$emailErr = "郵箱是必需的";
}
else
{
$email = test_input($_POST["email"]);
// 檢測郵箱是否合法
if (!preg_match("/([\w\-]+\@[\w\-]+\.[\w\-]+)/",$email))
{
$emailErr = "非法郵箱格式";
}
}
if (empty($_POST["website"]))
{
$website = "";
}
else
{
$website = test_input($_POST["website"]);
// 檢測 URL 地址是否合法
if (!preg_match("/\b(?:(?:https?|ftp):\/\/|www\.)[-a-z0-9+&@#\/%?=~_|!:,.;]*[-a-z0-9+&@#\/%=~_|]/i",$website))
{
$websiteErr = "非法的 URL 的地址";
}
}
if (empty($_POST["comment"]))
{
$comment = "";
}
else
{
$comment = test_input($_POST["comment"]);
}
if (empty($_POST["gender"]))
{
$genderErr = "性別是必需的";
}
else
{
$gender = test_input($_POST["gender"]);
}
}
function test_input($data)
{
$data = trim($data);
$data = stripslashes($data);
$data = htmlspecialchars($data);
return $data;
}
?>
<h2>PHP 表單驗證實例</h2>
<p><span class="error">* 必需字段。</span></p>
<form method="post" action="">
名字: <input type="text" name="name" value="<?php echo $name;?>">
<span class="error">* <?php echo $nameErr;?></span>
<br><br>
E-mail: <input type="text" name="email" value="<?php echo $email;?>">
<span class="error">* <?php echo $emailErr;?></span>
<br><br>
網(wǎng)址: <input type="text" name="website" value="<?php echo $website;?>">
<span class="error"><?php echo $websiteErr;?></span>
<br><br>
備注: <textarea name="comment" rows="5" cols="40"><?php echo $comment;?></textarea>
<br><br>
性別:
<input type="radio" name="gender" <?php if (isset($gender) && $gender=="female") echo "checked";?> value="female">女
<input type="radio" name="gender" <?php if (isset($gender) && $gender=="male") echo "checked";?> value="male">男
<span class="error">* <?php echo $genderErr;?></span>
<br><br>
<input type="submit" name="submit" value="Submit">
</form>
<?php
echo "<h2>您輸入的內(nèi)容是:</h2>";
echo $name;
echo "<br>";
echo $email;
echo "<br>";
echo $website;
echo "<br>";
echo $comment;
echo "<br>";
echo $gender;
?>
</body>
</html>In the above case: form validation has its own rules
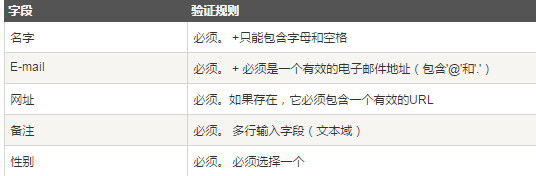
Text field
The "Name", "E-mail", and "Website" fields are text input elements, and the "Remarks" field is a textarea. The HTML code is as follows:
"Name": <input type="text" name="name">
E-mail: <input type="text" name="email">
Website: <input type="text" name="website">
Remarks: <textarea name="comment" rows="5" cols="40" ></textarea>
##
Radio button
The "Gender" field is a radio button, and the HTML code is as follows:
gender:<input type="radio" name="gender" value="female">Female
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?Male
Use php to validate the form
#When the user submits the form, we will do the following two things: Use the PHP trim() function to remove unnecessary characters (such as spaces, tabs, newlines) in the user input data. Use the PHP stripslashes() function to remove backslashes (\) from user input data
<!DOCTYPE HTML>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>php中文網(wǎng)</title>
</head>
<body>
<?php
// 定義變量并默認(rèn)設(shè)置為空值
$name = $email = $gender = $comment = $website = "";
if ($_SERVER["REQUEST_METHOD"] == "POST")
{
$name = test_input($_POST["name"]);
$email = test_input($_POST["email"]);
$website = test_input($_POST["website"]);
$comment = test_input($_POST["comment"]);
$gender = test_input($_POST["gender"]);
}
function test_input($data)
{
$data = trim($data);
$data = stripslashes($data);
$data = htmlspecialchars($data);
return $data;
}
?>
<h2>PHP 表單驗證實例</h2>
<form method="post" action="">
名字: <input type="text" name="name">
<br><br>
E-mail: <input type="text" name="email">
<br><br>
網(wǎng)址: <input type="text" name="website">
<br><br>
備注: <textarea name="comment" rows="5" cols="40"></textarea>
<br><br>
性別:
<input type="radio" name="gender" value="female">女
<input type="radio" name="gender" value="male">男
<br><br>
<input type="submit" name="submit" value="Submit">
</form>
<?php
echo "<h2>您輸入的內(nèi)容是:</h2>";
echo $name;
echo "<br>";
echo $email;
echo "<br>";
echo $website;
echo "<br>";
echo $comment;
echo "<br>";
echo $gender;
?>
</body>Note When we execute the above script, we will use $_SERVER["REQUEST_METHOD"] to detect whether the form has been submitted. If REQUEST_METHOD is POST, the form will be submitted - and the data will be validated. If the form is not submitted validation will be skipped and displayed blank. The use of input items in the above examples is optional, and it can be displayed normally even if the user does not enter any data.
#














