 Backend Development
Backend Development
 PHP Tutorial
PHP Tutorial
 Detailed explanation of inherited access type control of classes in PHP objects
Detailed explanation of inherited access type control of classes in PHP objects
Detailed explanation of inherited access type control of classes in PHP objects
Jul 02, 2017 am 11:32 AMType of Access control Allows developers to restrict access to members in a class by using modifiers. This is a new feature of PHP5 and an important feature in OOP languages. Most OOP languages ??already support this feature. PHP5 supports the following three access modifiers, two of which we have introduced in class encapsulation. To summarize here, Access control modifiers include public (public, default), private (private) and protected (protected). Their functions and the differences between them are shown in the following table:
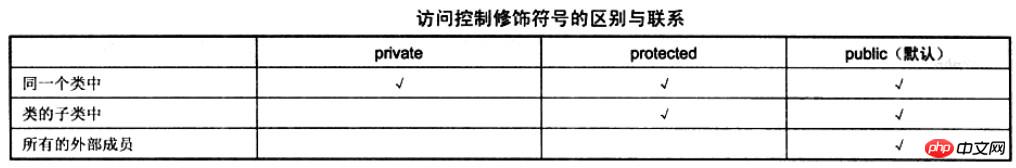
①Public access modifier public
Use this With this modifier, the members in the class will have no access restrictions, and all external members can access the members in this class. In all versions before PHP5, the members of the class in PHP are public.
②Private access modifier private
When a member of a class is defined as private, there are no access restrictions for all members of the same class, but for the External code of the class is not allowed to change or even operate, and subclasses of the class cannot access private-modified members. The code is as follows:
<?php
//聲明一個類作為父類使用,將它的成員都聲明為私有的
class MyClass {
private $var1=100;
private function printHello(){
echo "hello<br>";
}
}
//聲明一個Myclass類的子類師徒訪問父類中的私有成員
class MyClass2 extends MyClass{
function useProperty(){
echo "輸出從父類繼承過來的成員屬性值".$this ->var1."<br>";
$this ->printHello();
}
}
$subObj = new MyClass2();
$subObj -> useProperty(); //調(diào)用子類對象中的方法實現(xiàn)對父類私有成員的訪問
?>
In the above code, a class MyClass is declared, a private member attribute and a private member method are declared in the class, and A class MyClass2 is declared to inherit the class MyClass, and the private members in the parent class are accessed in the subclass MyClass2. But the private members in the parent class can only be used in its own class, so the access error occurs.
③Protected access modifier protected
Members modified as protected have access to subclasses of this class and subclasses of subclasses Permissions allow you to read and write properties and methods. But it cannot be accessed by external code of this class, and external code of this subclass does not have additional permissions to its properties and methods. By changing the access rights of the parent class in the above example to protected, the members of the parent class can be accessed in the subclass, but they cannot be accessed outside the class, so the purpose of encapsulating the object can also be completed. The code is as follows:
<?php
class MyClass {
protected $var1=100;
protected function printHello(){
echo "hello<br>";
}
}
//聲明一個Myclass類的子類師徒訪問父類中的保護成員
class MyClass2 extends MyClass{
function useProperty(){
echo "輸出從父類繼承過來的成員屬性值".$this ->var1."<br>";
$this ->printHello();
}
}
$subObj = new MyClass2();
$subObj -> useProperty(); //調(diào)用子類對象中的方法實現(xiàn)對父類私有成員的訪問
echo $subObj ->var1; //試圖訪問類中受保護的成員,結果出錯
?>In the above example, the members in the class MyClass are set to protected using the protected modifier, and they can be accessed directly in the subclass. But it is an error to access protected modified members outside the subclass. The above is the detailed content of Detailed explanation of inherited access type control of classes in PHP objects. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 How to upgrade PHP version?
Jun 27, 2025 am 02:14 AM
How to upgrade PHP version?
Jun 27, 2025 am 02:14 AM
Upgrading the PHP version is actually not difficult, but the key lies in the operation steps and precautions. The following are the specific methods: 1. Confirm the current PHP version and running environment, use the command line or phpinfo.php file to view; 2. Select the suitable new version and install it. It is recommended to install it with 8.2 or 8.1. Linux users use package manager, and macOS users use Homebrew; 3. Migrate configuration files and extensions, update php.ini and install necessary extensions; 4. Test whether the website is running normally, check the error log to ensure that there is no compatibility problem. Follow these steps and you can successfully complete the upgrade in most situations.
 How do I prevent cross-site request forgery (CSRF) attacks in PHP?
Jun 28, 2025 am 02:25 AM
How do I prevent cross-site request forgery (CSRF) attacks in PHP?
Jun 28, 2025 am 02:25 AM
TopreventCSRFattacksinPHP,implementanti-CSRFtokens.1)Generateandstoresecuretokensusingrandom_bytes()orbin2hex(random_bytes(32)),savethemin$_SESSION,andincludetheminformsashiddeninputs.2)ValidatetokensonsubmissionbystrictlycomparingthePOSTtokenwiththe
 PHP beginner guide: Detailed explanation of local environment configuration
Jun 27, 2025 am 02:09 AM
PHP beginner guide: Detailed explanation of local environment configuration
Jun 27, 2025 am 02:09 AM
To set up a PHP development environment, you need to select the appropriate tools and install the configuration correctly. ①The most basic PHP local environment requires three components: the web server (Apache or Nginx), the PHP itself and the database (such as MySQL/MariaDB); ② It is recommended that beginners use integration packages such as XAMPP or MAMP, which simplify the installation process. XAMPP is suitable for Windows and macOS. After installation, the project files are placed in the htdocs directory and accessed through localhost; ③MAMP is suitable for Mac users and supports convenient switching of PHP versions, but the free version has limited functions; ④ Advanced users can manually install them by Homebrew, in macOS/Linux systems
 How to combine two php arrays unique values?
Jul 02, 2025 pm 05:18 PM
How to combine two php arrays unique values?
Jul 02, 2025 pm 05:18 PM
To merge two PHP arrays and keep unique values, there are two main methods. 1. For index arrays or only deduplication, use array_merge and array_unique combinations: first merge array_merge($array1,$array2) and then use array_unique() to deduplicate them to finally get a new array containing all unique values; 2. For associative arrays and want to retain key-value pairs in the first array, use the operator: $result=$array1 $array2, which will ensure that the keys in the first array will not be overwritten by the second array. These two methods are applicable to different scenarios, depending on whether the key name is retained or only the focus is on
 How to use php exit function?
Jul 03, 2025 am 02:15 AM
How to use php exit function?
Jul 03, 2025 am 02:15 AM
exit() is a function in PHP that is used to terminate script execution immediately. Common uses include: 1. Terminate the script in advance when an exception is detected, such as the file does not exist or verification fails; 2. Output intermediate results during debugging and stop execution; 3. Call exit() after redirecting in conjunction with header() to prevent subsequent code execution; In addition, exit() can accept string parameters as output content or integers as status code, and its alias is die().
 Applying Semantic Structure with article, section, and aside in HTML
Jul 05, 2025 am 02:03 AM
Applying Semantic Structure with article, section, and aside in HTML
Jul 05, 2025 am 02:03 AM
The rational use of semantic tags in HTML can improve page structure clarity, accessibility and SEO effects. 1. Used for independent content blocks, such as blog posts or comments, it must be self-contained; 2. Used for classification related content, usually including titles, and is suitable for different modules of the page; 3. Used for auxiliary information related to the main content but not core, such as sidebar recommendations or author profiles. In actual development, labels should be combined and other, avoid excessive nesting, keep the structure simple, and verify the rationality of the structure through developer tools.
 How do I access session data in PHP?
Jun 30, 2025 am 01:33 AM
How do I access session data in PHP?
Jun 30, 2025 am 01:33 AM
To access session data in PHP, you must first start the session and then operate through the $_SESSION hyperglobal array. 1. The session must be started using session_start(), and the function must be called before any output; 2. When accessing session data, check whether the key exists. You can use isset($_SESSION['key']) or array_key_exists('key',$_SESSION); 3. Set or update session variables only need to assign values ??to the $_SESSION array without manually saving; 4. Clear specific data with unset($_SESSION['key']), clear all data and set $_SESSION to an empty array.
 What are recursive functions in PHP?
Jun 29, 2025 am 02:02 AM
What are recursive functions in PHP?
Jun 29, 2025 am 02:02 AM
Recursive functions refer to self-call functions in PHP. The core elements are 1. Defining the termination conditions (base examples), 2. Decomposing the problem and calling itself recursively (recursive examples). It is suitable for dealing with hierarchical structures, disassembling duplicate subproblems, or improving code readability, such as calculating factorials, traversing directories, etc. However, it is necessary to pay attention to the risks of memory consumption and stack overflow. When writing, the exit conditions should be clarified, the basic examples should be gradually approached, the redundant parameters should be avoided, and small inputs should be tested. For example, when scanning a directory, the function encounters a subdirectory and calls itself recursively until all levels are traversed.





