This blog post demonstrates building an AI agent for web searches using LangChain and Llama 3.3, a powerful large language model. The agent leverages external knowledge bases like ArXiv and Wikipedia to provide comprehensive answers.
Key Learning Outcomes
This tutorial will teach you:
- How to create a web-searching AI agent with LangChain and Llama 3.3.
- Integrating external data sources such as ArXiv and Wikipedia into your agent.
- Setting up the development environment and required tools.
- Implementing modularity and error handling for robust application development.
- Utilizing Streamlit to create a user-friendly interface for your AI agent.
This article is part of the Data Science Blogathon.
Table of Contents
- Understanding Llama 3.3
- Introducing LangChain
- Core Components of the Web-Searching Agent
- Workflow Diagram
- Environment Setup and Configuration
- Conclusion
- Frequently Asked Questions
Understanding Llama 3.3
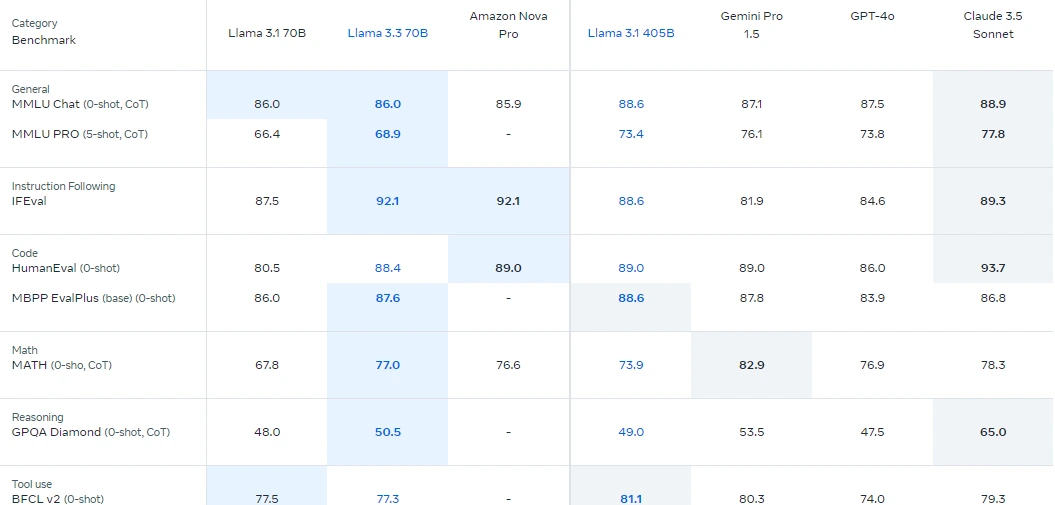
Llama 3.3, a 70-billion parameter instruction-tuned LLM from Meta, excels at text-based tasks. Its improvements over previous versions (Llama 3.1 70B and Llama 3.2 90B) and cost-effectiveness make it a compelling choice. It even rivals larger models in certain areas.
Llama 3.3 Features:
- Instruction Tuning: Precise instruction following.
- Multilingual Support: Handles multiple languages, including English, Spanish, French, German, Hindi, Portuguese, Italian, and Thai.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Affordable high-performance.
- Accessibility: Deployable on various hardware configurations, including CPUs.
Introducing LangChain
LangChain is an open-source framework for developing LLM-powered applications. It simplifies LLM integration, allowing for the creation of sophisticated AI solutions.
LangChain Key Features:
- Chainable Components: Build complex workflows by linking components.
- Tool Integration: Easily integrate tools and APIs.
- Memory Management: Maintain conversational context.
- Extensibility: Supports custom components and integrations.
Core Components of the Web-Searching Agent
Our agent uses:
- LLM (Llama 3.3): The core processing unit.
- Search Tool: Accesses web search engines (using an API).
- Prompt Template: Structures input for the LLM.
- Agent Executor: Orchestrates LLM and tool interaction.
Workflow Diagram
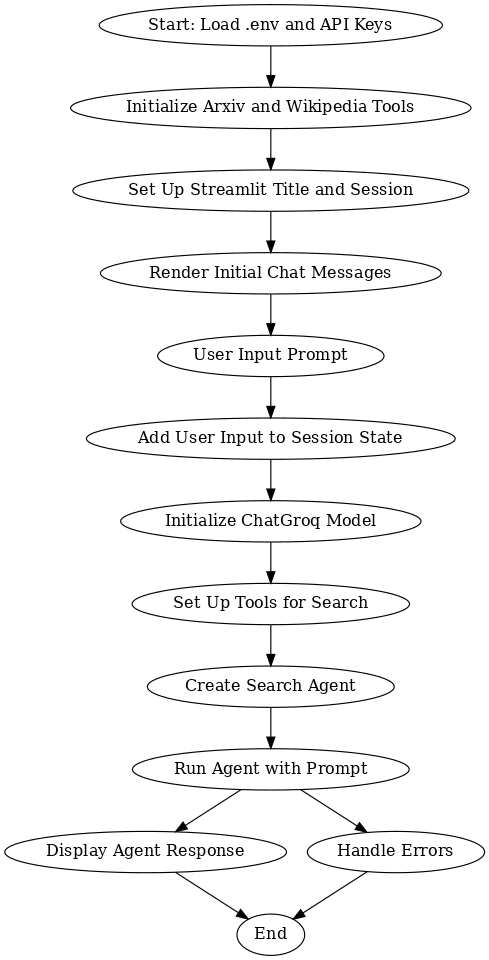
This diagram illustrates the interaction between the user, the LLM, and the data sources (ArXiv, Wikipedia). It shows how user queries are processed, information is retrieved, and responses are generated. Error handling is also incorporated.
Environment Setup and Configuration
This section details setting up the development environment, installing dependencies, and configuring API keys. It includes code snippets for creating a virtual environment, installing packages, and setting up a .env file for secure API key management. The code examples demonstrate importing necessary libraries, loading environment variables, and configuring ArXiv and Wikipedia tools. The Streamlit app setup, including handling user input and displaying chat messages, is also covered. Finally, the code shows how to initialize the LLM, tools, and the search agent, and how to generate and display the assistant's response, including error handling. Example outputs are also provided.
Conclusion
This project showcases the power of combining LLMs like Llama 3.3 with external knowledge sources using LangChain. The modular design allows for easy expansion and adaptation to various domains. Streamlit simplifies the creation of interactive user interfaces.
Key Takeaways:
- Combining LLMs and external knowledge sources creates powerful AI agents.
- Streamlit simplifies interactive web app development.
- Environment variables enhance security.
- Error handling improves application reliability.
- Modular design allows for easy extension.
Frequently Asked Questions
- Q1. What is Llama 3.3? A powerful LLM used for its reasoning and natural language generation capabilities.
- Q2. Why ArXiv and Wikipedia? Access to research papers and general knowledge.
- Q3. How does Streamlit help? Provides an easy-to-use chat interface.
- Q4. Is the app limited to these sources? No, it's easily extensible.
- Q5. How are errors handled? Using try-except blocks for graceful error handling.
(Note: Images are not included in this response as they were not provided in a format suitable for direct inclusion. The image URLs remain as placeholders.)
The above is the detailed content of Building a Web-Searching Agent. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1794
1794
 16
16
 1739
1739
 56
56
 1590
1590
 29
29
 1468
1468
 72
72
 267
267
 587
587
 AI Investor Stuck At A Standstill? 3 Strategic Paths To Buy, Build, Or Partner With AI Vendors
Jul 02, 2025 am 11:13 AM
AI Investor Stuck At A Standstill? 3 Strategic Paths To Buy, Build, Or Partner With AI Vendors
Jul 02, 2025 am 11:13 AM
Investing is booming, but capital alone isn’t enough. With valuations rising and distinctiveness fading, investors in AI-focused venture funds must make a key decision: Buy, build, or partner to gain an edge? Here’s how to evaluate each option—and pr
 AGI And AI Superintelligence Are Going To Sharply Hit The Human Ceiling Assumption Barrier
Jul 04, 2025 am 11:10 AM
AGI And AI Superintelligence Are Going To Sharply Hit The Human Ceiling Assumption Barrier
Jul 04, 2025 am 11:10 AM
Let’s talk about it. This analysis of an innovative AI breakthrough is part of my ongoing Forbes column coverage on the latest in AI, including identifying and explaining various impactful AI complexities (see the link here). Heading Toward AGI And
 Kimi K2: The Most Powerful Open-Source Agentic Model
Jul 12, 2025 am 09:16 AM
Kimi K2: The Most Powerful Open-Source Agentic Model
Jul 12, 2025 am 09:16 AM
Remember the flood of open-source Chinese models that disrupted the GenAI industry earlier this year? While DeepSeek took most of the headlines, Kimi K1.5 was one of the prominent names in the list. And the model was quite cool.
 Grok 4 vs Claude 4: Which is Better?
Jul 12, 2025 am 09:37 AM
Grok 4 vs Claude 4: Which is Better?
Jul 12, 2025 am 09:37 AM
By mid-2025, the AI “arms race” is heating up, and xAI and Anthropic have both released their flagship models, Grok 4 and Claude 4. These two models are at opposite ends of the design philosophy and deployment platform, yet they
 Future Forecasting A Massive Intelligence Explosion On The Path From AI To AGI
Jul 02, 2025 am 11:19 AM
Future Forecasting A Massive Intelligence Explosion On The Path From AI To AGI
Jul 02, 2025 am 11:19 AM
Let’s talk about it. This analysis of an innovative AI breakthrough is part of my ongoing Forbes column coverage on the latest in AI, including identifying and explaining various impactful AI complexities (see the link here). For those readers who h
 AMD Keeps Building Momentum In AI, With Plenty Of Work Still To Do
Jun 28, 2025 am 11:15 AM
AMD Keeps Building Momentum In AI, With Plenty Of Work Still To Do
Jun 28, 2025 am 11:15 AM
Overall, I think the event was important for showing how AMD is moving the ball down the field for customers and developers. Under Su, AMD’s M.O. is to have clear, ambitious plans and execute against them. Her “say/do” ratio is high. The company does
 Chain Of Thought For Reasoning Models Might Not Work Out Long-Term
Jul 02, 2025 am 11:18 AM
Chain Of Thought For Reasoning Models Might Not Work Out Long-Term
Jul 02, 2025 am 11:18 AM
For example, if you ask a model a question like: “what does (X) person do at (X) company?” you may see a reasoning chain that looks something like this, assuming the system knows how to retrieve the necessary information:Locating details about the co
 Batch Processing vs Mini-Batch Training in Deep Learning
Jun 30, 2025 am 09:46 AM
Batch Processing vs Mini-Batch Training in Deep Learning
Jun 30, 2025 am 09:46 AM
Deep learning has revolutionised the AI field by allowing machines to grasp more in-depth information within our data. Deep learning has been able to do this by replicating how our brain functions through the logic of neuron syna




