In CSS, z-index means "level, layer space stacking level", which can specify the stacking order of an element, which is used to confirm the stacking level of the element in the current stacking context, with higher stacking Sequential elements will always appear before elements lower in the stacking order; syntax "element {z-index: auto|
}".

The operating environment of this tutorial: Windows 7 system, CSS3&&HTML5 version, Dell G3 computer.
css z-index
z-index :auto|<integer>
auto default value
Definition: The stacking order of an element in the document, used to confirm the stacking level of the element in the current stacking context.
Applies to: positioned elements. That is to say, elements whose position is non-static are defined
The stacking order of each element is determined by the stacking context to which it belongs and the stacking level of the element itself (each element only belongs to one stacking context).
1. The same cascading context
The larger cascading level is displayed above, and the smaller level is displayed below;
The two elements in the cascading level are displayed according to their HTML In the order of the document flow, what is written later will overwrite the previous one.
2. Different cascading contexts
The display order of elements is determined by the cascading level of their ancestors, regardless of their own cascading level.
Example:
1. There are two p boxes, a and c are in one box, and b is in another box. Consider that the z-index is Not a normal effect.
<body>
<div>
<p class="a">a</p>
<p class="c">c</p>
</div>
<div>
<p class="b">b</p>
</div>
</body>p z-index is not set, and a new local cascading context will not be generated under advanced browsers. That is to say, their child elements are not wrapped by the new local cascading context, so their child elements will In the same stacking context, the display order can be determined directly by its own stacking level.
div {
position: relative;
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
}
p {
position: absolute;
font-size: 20px;
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
}
.a {
background-color: pink;
z-index: 1;
}
.c {
background-color: green;
z-index: 2;
top: 20px;
left: 20px;
}
.b {
background-color: red;
z-index: 3;
top: -20px;
left: 40px;
}a, b, and c are in a stacking context, so the level is determined based on the z-index size. As shown in the figure below:
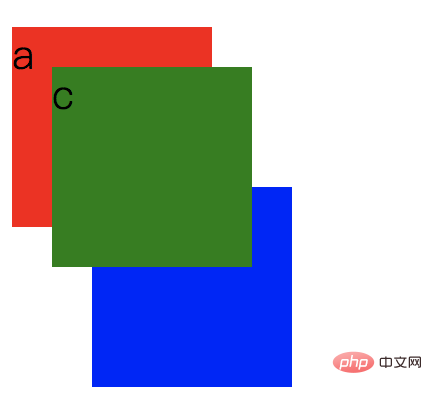
2. There are two p boxes, a and c are in one box, and b is in another box. Consider that its z-index is Not a normal effect.
<body> <div class="box1"> <p class="a">a</p> <p class="c">c</p> </div> <div class="box2"> <p class="b">b</p> </div> </body>
p sets z-index, then the child elements in p are mainly based on the cascading relationship of the parent element.
<style type="text/css">
div {
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
position: relative;
}
.box1 {
z-index: 2;
}
.box2 {
z-index: 1;
}
p {
position: absolute;
font-size: 20px;
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
}
.a {
background-color: red;
}
.c {
background-color: green;
top: 20px;
left: 20px;
}
.b {
background-color: blue;
top: -20px;
left: 40px;
z-index: 20;
}
</style>a, b, and c are in different stacking contexts, so the level is determined based on the z-index size of the parent. As shown in the figure below:

From the above, we can see how z-index is determined: the stacking context to which it belongs and the stacking level of the element itself
Update For more programming-related knowledge, please visit: programming learning website! !
The above is the detailed content of What does z-index mean in css?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 How to use the new semantic tags (such as section, article) in HTML5?
May 23, 2025 pm 11:36 PM
How to use the new semantic tags (such as section, article) in HTML5?
May 23, 2025 pm 11:36 PM
The reason we use semantic tags is that they improve SEO, enhance accessibility, and code maintainability. 1. Include titles when using them to avoid abuse. 2. Use stand-alone content blocks, suitable for blogs or news. 3. Pay attention to the nesting and SEO of tags, and do not pile up tags for SEO.
 How can I include the CSS with React?
May 26, 2025 am 12:01 AM
How can I include the CSS with React?
May 26, 2025 am 12:01 AM
There are five ways to include CSS in React: 1. Use inline styles, which are simple but not conducive to reuse and maintenance; 2. Use CSS files, which are implemented through import, which are conducive to organization but may lead to conflicts; 3. Use CSSModules to avoid global conflicts but require configuration; 4. Use StyledComponents to dynamically generate styles using JavaScript but require dependency on libraries; 5. Use Sass or Less to provide more functions but increase construction complexity.
 How can I include CSS only on some pages?
Jun 11, 2025 am 12:01 AM
How can I include CSS only on some pages?
Jun 11, 2025 am 12:01 AM
There are three ways to selectively include CSS on a specific page: 1. Inline CSS, suitable for pages that are not frequently accessed or require unique styles; 2. Load external CSS files using JavaScript conditions, suitable for situations where flexibility is required; 3. Containment on the server side, suitable for scenarios using server-side languages. This approach can optimize website performance and maintainability, but requires balance of modularity and performance.
 CSS Inclusion Methods: Pros, Cons, and Examples
Jun 07, 2025 am 12:03 AM
CSS Inclusion Methods: Pros, Cons, and Examples
Jun 07, 2025 am 12:03 AM
ThedifferentmethodsforincludingCSSinawebpageareinline,internal,andexternalCSS.1)InlineCSS:Easytoimplementbutleadstounmaintainablecode.2)InternalCSS:MoreorganizedthaninlinebutcanclutterHTML.3)ExternalCSS:Bestforlargerprojects,promotesmaintainabilityan
 HTML, CSS, and JavaScript: How They Work Together
May 27, 2025 am 12:05 AM
HTML, CSS, and JavaScript: How They Work Together
May 27, 2025 am 12:05 AM
HTML, CSS and JavaScript are responsible for structure, style and dynamic functions in web development respectively. 1. HTML defines the web structure, 2. CSS is responsible for style and layout, 3. JavaScript provides dynamic interaction and functions.
 What is the purpose of the z-index property, and how does it affect stacking contexts?
Jun 09, 2025 am 12:16 AM
What is the purpose of the z-index property, and how does it affect stacking contexts?
Jun 09, 2025 am 12:16 AM
z-index is used in CSS to control the stacking order of elements, but its effect is limited by the "stacking context". 1.z-index only takes effect in the same stacking context, and the higher the value, the higher the value. 2. The stacking context is created by specific conditions, such as positioning elements to set z-index, transparency, transformation, filters, etc. 3. Children elements are always stacked in the parent context and cannot break through the parent hierarchy. 4. When using z-index, avoid abuse of high values, adopt meaningful hierarchy ranges, and check whether the parent element affects stacking. 5. When encountering problems, DOM structure and style should be reviewed to confirm the context relationship. The key to understanding z-index lies in mastering the mechanism of stacking context.
 Best Practices for Including CSS in Your Website
May 24, 2025 am 12:09 AM
Best Practices for Including CSS in Your Website
May 24, 2025 am 12:09 AM
ThebestpracticesforincludingCSSinawebsiteare:1)UseexternalCSSforseparationofcontentandpresentation,reusability,andcachingbenefits.2)ConsiderusingCSSpreprocessorslikeSassorLessformodularity.3)OptimizeperformancewithCSSminificationandcompression.4)Stru
 How to deal with CSS and Case-sensitivity
May 25, 2025 am 12:02 AM
How to deal with CSS and Case-sensitivity
May 25, 2025 am 12:02 AM
CSSismostlycase-insensitive,butselectorsandcustompropertiesarecase-sensitive.1)Useconsistentcasingconventions.2)EmploylinterslikeStylelint.3)Testacrossbrowsers.4)Bemindfulofexternalresources'conventions.Consistentcasinghelpsmaintaincodecleanlinessand






