Tutorial on writing a simple chat program in Python
May 08, 2023 pm 06:37 PMImplementation ideas
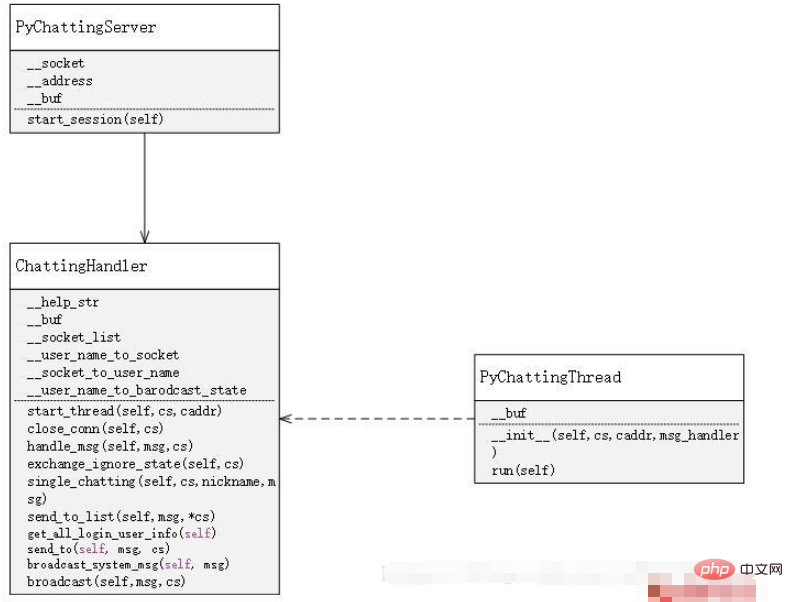
x01 Establishment of the server
First, on the server side, use socket to accept messages. Every time a socket request is accepted, a socket is opened. A new thread is used to manage the distribution and acceptance of messages. At the same time, there is a handler to manage all threads, thereby realizing the processing of various functions of the chat room
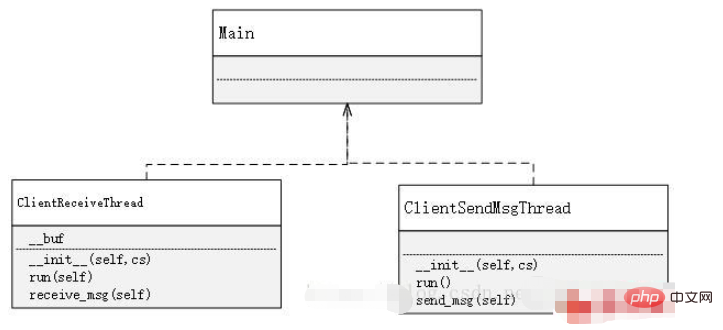
x02 Establishment of the client
The establishment of the client is much simpler than the server. The function of the client is only to send and receive messages, and to enter specific characters according to specific rules to achieve the use of different functions. Therefore, in On the client side, you only need to use two threads, one is dedicated to receiving messages, and the other is dedicated to sending messages. As for why not use one, that is because, if you only use one, then After receiving a message, the one that receives the message is in a blocked state before sending it. Similarly, the same is true for sending a message. If these two functions are implemented in one place, it will make it impossible to continuously send or receive messages.
Implementation method
Server-side implementation
import?json
import?threading
from?socket?import?*
from?time?import?ctime
class?PyChattingServer:
????__socket?=?socket(AF_INET,?SOCK_STREAM,?0)
????__address?=?('',?12231)
????__buf?=?1024
????def?__init__(self):
????????self.__socket.bind(self.__address)
????????self.__socket.listen(20)
????????self.__msg_handler?=?ChattingHandler()
????def?start_session(self):
????????print('等待客戶連接...\r\n')
????????try:
????????????while?True:
????????????????cs,?caddr?=?self.__socket.accept()
????????????????#?利用handler來管理線程,實(shí)現(xiàn)線程之間的socket的相互通信
????????????????self.__msg_handler.start_thread(cs,?caddr)
????????except?socket.error:
????????????pass
class?ChattingThread(threading.Thread):
????__buf?=?1024
????def?__init__(self,?cs,?caddr,?msg_handler):
????????super(ChattingThread,?self).__init__()
????????self.__cs?=?cs
????????self.__caddr?=?caddr
????????self.__msg_handler?=?msg_handler
????#?使用多線程管理會(huì)話
????def?run(self):
????????try:
????????????print('...連接來自于:',?self.__caddr)
????????????data?=?'歡迎你到來PY_CHATTING!請(qǐng)輸入你的很cooooool的昵稱(不能帶有空格喲`)\r\n'
????????????self.__cs.sendall(bytes(data,?'utf-8'))
????????????while?True:
????????????????data?=?self.__cs.recv(self.__buf).decode('utf-8')
????????????????if?not?data:
????????????????????break
????????????????self.__msg_handler.handle_msg(data,?self.__cs)
????????????????print(data)
????????except?socket.error?as?e:
????????????print(e.args)
????????????pass
????????finally:
????????????self.__msg_handler.close_conn(self.__cs)
????????????self.__cs.close()
class?ChattingHandler:
????__help_str?=?"[?SYSTEM?]\r\n"?\
?????????????????"輸入/ls,即可獲得所有登陸用戶信息\r\n"?\
?????????????????"輸入/h,即可獲得幫助\r\n"?\
?????????????????"輸入@用戶名?(注意用戶名后面的空格)+消息,即可發(fā)動(dòng)單聊\r\n"?\
?????????????????"輸入/i,即可屏蔽群聊信息\r\n"?\
?????????????????"再次輸入/i,即可取消屏蔽\r\n"?\
?????????????????"所有首字符為/的信息都不會(huì)發(fā)送出去"
????__buf?=?1024
????__socket_list?=?[]
????__user_name_to_socket?=?{}
????__socket_to_user_name?=?{}
????__user_name_to_broadcast_state?=?{}
????def?start_thread(self,?cs,?caddr):
????????self.__socket_list.append(cs)
????????chat_thread?=?ChattingThread(cs,?caddr,?self)
????????chat_thread.start()
????def?close_conn(self,?cs):
????????if?cs?not?in?self.__socket_list:
????????????return
????????#?去除socket的記錄
????????nickname?=?"SOMEONE"
????????if?cs?in?self.__socket_list:
????????????self.__socket_list.remove(cs)
????????#?去除socket與username之間的映射關(guān)系
????????if?cs?in?self.__socket_to_user_name:
????????????nickname?=?self.__socket_to_user_name[cs]
????????????self.__user_name_to_socket.pop(self.__socket_to_user_name[cs])
????????????self.__socket_to_user_name.pop(cs)
????????????self.__user_name_to_broadcast_state.pop(nickname)
????????nickname?+=?"?"
????????#?廣播某玩家退出聊天室
????????self.broadcast_system_msg(nickname?+?"離開了PY_CHATTING")
????#?管理用戶輸入的信息
????def?handle_msg(self,?msg,?cs):
????????js?=?json.loads(msg)
????????if?js['type']?==?"login":
????????????if?js['msg']?not?in?self.__user_name_to_socket:
????????????????if?'?'?in?js['msg']:
????????????????????self.send_to(json.dumps({
????????????????????????'type':?'login',
????????????????????????'success':?False,
????????????????????????'msg':?'賬號(hào)不能夠帶有空格'
????????????????????}),?cs)
????????????????else:
????????????????????self.__user_name_to_socket[js['msg']]?=?cs
????????????????????self.__socket_to_user_name[cs]?=?js['msg']
????????????????????self.__user_name_to_broadcast_state[js['msg']]?=?True
????????????????????self.send_to(json.dumps({
????????????????????????'type':?'login',
????????????????????????'success':?True,
????????????????????????'msg':?'昵稱建立成功,輸入/ls可查看所有在線的人,輸入/help可以查看幫助(所有首字符為/的消息都不會(huì)發(fā)送)'
????????????????????}),?cs)
????????????????????#?廣播其他人,他已經(jīng)進(jìn)入聊天室
????????????????????self.broadcast_system_msg(js['msg']?+?"已經(jīng)進(jìn)入了聊天室")
????????????else:
????????????????self.send_to(json.dumps({
????????????????????'type':?'login',
????????????????????'success':?False,
????????????????????'msg':?'賬號(hào)已存在'
????????????????}),?cs)
????????#?若玩家處于屏蔽模式,則無法發(fā)送群聊消息
????????elif?js['type']?==?"broadcast":
????????????if?self.__user_name_to_broadcast_state[self.__socket_to_user_name[cs]]:
????????????????self.broadcast(js['msg'],?cs)
????????????else:
????????????????self.send_to(json.dumps({
????????????????????'type':?'broadcast',
????????????????????'msg':?'屏蔽模式下無法發(fā)送群聊信息'
????????????????}),?cs)
????????elif?js['type']?==?"ls":
????????????self.send_to(json.dumps({
????????????????'type':?'ls',
????????????????'msg':?self.get_all_login_user_info()
????????????}),?cs)
????????elif?js['type']?==?"help":
????????????self.send_to(json.dumps({
????????????????'type':?'help',
????????????????'msg':?self.__help_str
????????????}),?cs)
????????elif?js['type']?==?"sendto":
????????????self.single_chatting(cs,?js['nickname'],?js['msg'])
????????elif?js['type']?==?"ignore":
????????????self.exchange_ignore_state(cs)
????def?exchange_ignore_state(self,?cs):
????????if?cs?in?self.__socket_to_user_name:
????????????state?=?self.__user_name_to_broadcast_state[self.__socket_to_user_name[cs]]
????????????if?state:
????????????????state?=?False
????????????else:
????????????????state?=?True
????????????self.__user_name_to_broadcast_state.pop(self.__socket_to_user_name[cs])
????????????self.__user_name_to_broadcast_state[self.__socket_to_user_name[cs]]?=?state
????????????if?self.__user_name_to_broadcast_state[self.__socket_to_user_name[cs]]:
????????????????msg?=?"通常模式"
????????????else:
????????????????msg?=?"屏蔽模式"
????????????self.send_to(json.dumps({
????????????????'type':?'ignore',
????????????????'success':?True,
????????????????'msg':?'[TIME?:?%s]\r\n[?SYSTEM?]?:?%s\r\n'?%?(ctime(),?"模式切換成功,現(xiàn)在是"?+?msg)
????????????}),?cs)
????????else:
????????????self.send_to({
????????????????'type':?'ignore',
????????????????'success':?False,
????????????????'msg':?'切換失敗'
????????????},?cs)
????def?single_chatting(self,?cs,?nickname,?msg):
????????if?nickname?in?self.__user_name_to_socket:
????????????msg?=?'[TIME?:?%s]\r\n[?%s?CHATTING?TO?%s?]?:?%s\r\n'?%?(
????????????????ctime(),?self.__socket_to_user_name[cs],?nickname,?msg)
????????????self.send_to_list(json.dumps({
????????????????'type':?'single',
????????????????'msg':?msg
????????????}),?self.__user_name_to_socket[nickname],?cs)
????????else:
????????????self.send_to(json.dumps({
????????????????'type':?'single',
????????????????'msg':?'該用戶不存在'
????????????}),?cs)
????????print(nickname)
????def?send_to_list(self,?msg,?*cs):
????????for?i?in?range(len(cs)):
????????????self.send_to(msg,?cs[i])
????def?get_all_login_user_info(self):
????????login_list?=?"[?SYSTEM?]?ALIVE?USER?:?\r\n"
????????for?key?in?self.__socket_to_user_name:
????????????login_list?+=?self.__socket_to_user_name[key]?+?",\r\n"
????????return?login_list
????def?send_to(self,?msg,?cs):
????????if?cs?not?in?self.__socket_list:
????????????self.__socket_list.append(cs)
????????cs.sendall(bytes(msg,?'utf-8'))
????def?broadcast_system_msg(self,?msg):
????????data?=?'[TIME?:?%s]\r\n[?SYSTEM?]?:?%s\r\n'?%?(ctime(),?msg)
????????js?=?json.dumps({
????????????'type':?'system_msg',
????????????'msg':?data
????????})
????????#?屏蔽了群聊的玩家也可以獲得系統(tǒng)的群發(fā)信息
????????for?i?in?range(len(self.__socket_list)):
????????????if?self.__socket_list[i]?in?self.__socket_to_user_name:
????????????????self.__socket_list[i].sendall(bytes(js,?'utf-8'))
????def?broadcast(self,?msg,?cs):
????????data?=?'[TIME?:?%s]\r\n[%s]?:?%s\r\n'?%?(ctime(),?self.__socket_to_user_name[cs],?msg)
????????js?=?json.dumps({
????????????'type':?'broadcast',
????????????'msg':?data
????????})
????????#?沒有的登陸的玩家無法得知消息,屏蔽了群聊的玩家也沒辦法獲取信息
????????for?i?in?range(len(self.__socket_list)):
????????????if?self.__socket_list[i]?in?self.__socket_to_user_name?\
????????????????????and?self.__user_name_to_broadcast_state[self.__socket_to_user_name[self.__socket_list[i]]]:
????????????????self.__socket_list[i].sendall(bytes(js,?'utf-8'))
def?main():
????server?=?PyChattingServer()
????server.start_session()
main()
 Client-side implementation
Client-side implementation
import?json
import?threading
from?socket?import?*
is_login?=?False
is_broadcast?=?True
class?ClientReceiveThread(threading.Thread):
????__buf?=?1024
????def?__init__(self,?cs):
????????super(ClientReceiveThread,?self).__init__()
????????self.__cs?=?cs
????def?run(self):
????????self.receive_msg()
????def?receive_msg(self):
????????while?True:
????????????msg?=?self.__cs.recv(self.__buf).decode('utf-8')
????????????if?not?msg:
????????????????break
????????????js?=?json.loads(msg)
????????????if?js['type']?==?"login":
????????????????if?js['success']:
????????????????????global?is_login
????????????????????is_login?=?True
????????????????print(js['msg'])
????????????elif?js['type']?==?"ignore":
????????????????if?js['success']:
????????????????????global?is_broadcast
????????????????????if?is_broadcast:
????????????????????????is_broadcast?=?False
????????????????????else:
????????????????????????is_broadcast?=?True
????????????????print(js['msg'])
????????????else:
????????????????if?not?is_broadcast:
????????????????????print("[現(xiàn)在處于屏蔽模式]")
????????????????print(js['msg'])
class?ClientSendMsgThread(threading.Thread):
????def?__init__(self,?cs):
????????super(ClientSendMsgThread,?self).__init__()
????????self.__cs?=?cs
????def?run(self):
????????self.send_msg()
????#?根據(jù)不同的輸入格式來進(jìn)行不同的聊天方式
????def?send_msg(self):
????????while?True:
????????????js?=?None
????????????msg?=?input()
????????????if?not?is_login:
????????????????js?=?json.dumps({
????????????????????'type':?'login',
????????????????????'msg':?msg
????????????????})
????????????elif?msg[0]?==?"@":
????????????????data?=?msg.split('?')
????????????????if?not?data:
????????????????????print("請(qǐng)重新輸入")
????????????????????break
????????????????nickname?=?data[0]
????????????????nickname?=?nickname.strip("@")
????????????????if?len(data)?==?1:
????????????????????data.append("?")
????????????????js?=?json.dumps({
????????????????????'type':?'sendto',
????????????????????'nickname':?nickname,
????????????????????'msg':?data[1]
????????????????})
????????????elif?msg?==?"/help":
????????????????js?=?json.dumps({
????????????????????'type':?'help',
????????????????????'msg':?None
????????????????})
????????????elif?msg?==?"/ls":
????????????????js?=?json.dumps({
????????????????????'type':?'ls',
????????????????????'msg':?None
????????????????})
????????????elif?msg?==?"/i":
????????????????js?=?json.dumps({
????????????????????'type':?'ignore',
????????????????????'msg':?None
????????????????})
????????????else:
????????????????if?msg[0]?!=?'/':
????????????????????js?=?json.dumps({
????????????????????????'type':?'broadcast',
????????????????????????'msg':?msg
????????????????????})
????????????if?js?is?not?None:
????????????????self.__cs.sendall(bytes(js,?'utf-8'))
def?main():
????buf?=?1024
????#?改變這個(gè)的地址,變成服務(wù)器的地址,那么只要部署到服務(wù)器上就可以全網(wǎng)使用了
????address?=?("127.0.0.1",?12231)
????cs?=?socket(AF_INET,?SOCK_STREAM,?0)
????cs.connect(address)
????data?=?cs.recv(buf).decode("utf-8")
????if?data:
????????print(data)
????receive_thread?=?ClientReceiveThread(cs)
????receive_thread.start()
????send_thread?=?ClientSendMsgThread(cs)
????send_thread.start()
????while?True:
????????pass
main()The above is the detailed content of Tutorial on writing a simple chat program in Python. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 Polymorphism in python classes
Jul 05, 2025 am 02:58 AM
Polymorphism in python classes
Jul 05, 2025 am 02:58 AM
Polymorphism is a core concept in Python object-oriented programming, referring to "one interface, multiple implementations", allowing for unified processing of different types of objects. 1. Polymorphism is implemented through method rewriting. Subclasses can redefine parent class methods. For example, the spoke() method of Animal class has different implementations in Dog and Cat subclasses. 2. The practical uses of polymorphism include simplifying the code structure and enhancing scalability, such as calling the draw() method uniformly in the graphical drawing program, or handling the common behavior of different characters in game development. 3. Python implementation polymorphism needs to satisfy: the parent class defines a method, and the child class overrides the method, but does not require inheritance of the same parent class. As long as the object implements the same method, this is called the "duck type". 4. Things to note include the maintenance
 2025 quantitative trading skills: Python's automatic brick-moving strategy, making a daily profit of 5% as stable as a dog!
Jul 03, 2025 am 10:27 AM
2025 quantitative trading skills: Python's automatic brick-moving strategy, making a daily profit of 5% as stable as a dog!
Jul 03, 2025 am 10:27 AM
The digital asset market attracts global attention with its high volatility. In this environment, how to steadily capture returns has become the goal pursued by countless participants. Quantitative trading, with its dependence on data and algorithm-driven characteristics, is becoming a powerful tool to deal with market challenges. Especially in 2025, this time node full of infinite possibilities is combined with the powerful programming language Python to build an automated "brick-moving" strategy, that is, to use the tiny price spreads between different trading platforms for arbitrage, which is considered a potential way to achieve efficient and stable profits.
 Python `@classmethod` decorator explained
Jul 04, 2025 am 03:26 AM
Python `@classmethod` decorator explained
Jul 04, 2025 am 03:26 AM
A class method is a method defined in Python through the @classmethod decorator. Its first parameter is the class itself (cls), which is used to access or modify the class state. It can be called through a class or instance, which affects the entire class rather than a specific instance; for example, in the Person class, the show_count() method counts the number of objects created; when defining a class method, you need to use the @classmethod decorator and name the first parameter cls, such as the change_var(new_value) method to modify class variables; the class method is different from the instance method (self parameter) and static method (no automatic parameters), and is suitable for factory methods, alternative constructors, and management of class variables. Common uses include:
 Understanding the Performance Differences Between Golang and Python for Web APIs
Jul 03, 2025 am 02:40 AM
Understanding the Performance Differences Between Golang and Python for Web APIs
Jul 03, 2025 am 02:40 AM
Golangofferssuperiorperformance,nativeconcurrencyviagoroutines,andefficientresourceusage,makingitidealforhigh-traffic,low-latencyAPIs;2.Python,whileslowerduetointerpretationandtheGIL,provideseasierdevelopment,arichecosystem,andisbettersuitedforI/O-bo
 Python Function Arguments and Parameters
Jul 04, 2025 am 03:26 AM
Python Function Arguments and Parameters
Jul 04, 2025 am 03:26 AM
Parameters are placeholders when defining a function, while arguments are specific values ??passed in when calling. 1. Position parameters need to be passed in order, and incorrect order will lead to errors in the result; 2. Keyword parameters are specified by parameter names, which can change the order and improve readability; 3. Default parameter values ??are assigned when defined to avoid duplicate code, but variable objects should be avoided as default values; 4. args and *kwargs can handle uncertain number of parameters and are suitable for general interfaces or decorators, but should be used with caution to maintain readability.
 Strategies for Integrating Golang Services with Existing Python Infrastructure
Jul 02, 2025 pm 04:39 PM
Strategies for Integrating Golang Services with Existing Python Infrastructure
Jul 02, 2025 pm 04:39 PM
TointegrateGolangserviceswithexistingPythoninfrastructure,useRESTAPIsorgRPCforinter-servicecommunication,allowingGoandPythonappstointeractseamlesslythroughstandardizedprotocols.1.UseRESTAPIs(viaframeworkslikeGininGoandFlaskinPython)orgRPC(withProtoco
 Explain Python generators and iterators.
Jul 05, 2025 am 02:55 AM
Explain Python generators and iterators.
Jul 05, 2025 am 02:55 AM
Iterators are objects that implement __iter__() and __next__() methods. The generator is a simplified version of iterators, which automatically implement these methods through the yield keyword. 1. The iterator returns an element every time he calls next() and throws a StopIteration exception when there are no more elements. 2. The generator uses function definition to generate data on demand, saving memory and supporting infinite sequences. 3. Use iterators when processing existing sets, use a generator when dynamically generating big data or lazy evaluation, such as loading line by line when reading large files. Note: Iterable objects such as lists are not iterators. They need to be recreated after the iterator reaches its end, and the generator can only traverse it once.
 Describe Python garbage collection in Python.
Jul 03, 2025 am 02:07 AM
Describe Python garbage collection in Python.
Jul 03, 2025 am 02:07 AM
Python's garbage collection mechanism automatically manages memory through reference counting and periodic garbage collection. Its core method is reference counting, which immediately releases memory when the number of references of an object is zero; but it cannot handle circular references, so a garbage collection module (gc) is introduced to detect and clean the loop. Garbage collection is usually triggered when the reference count decreases during program operation, the allocation and release difference exceeds the threshold, or when gc.collect() is called manually. Users can turn off automatic recycling through gc.disable(), manually execute gc.collect(), and adjust thresholds to achieve control through gc.set_threshold(). Not all objects participate in loop recycling. If objects that do not contain references are processed by reference counting, it is built-in






