C Language vs. C: Which Is Better for New Programmers
Mar 19, 2024 am 08:30 AM
C language or C: Which one is more suitable for programming novices
In the era of rapid development of modern technology, learning programming has become an increasingly popular choice, regardless of Either as part of career development or as a way to improve your logical thinking skills. Among many programming languages, C language and C are both very classic and representative languages. Many people are confused about how to choose C language or C as an entry-level programming language. So, is C language more suitable for programming novices, or is C more suitable? Specific code examples are needed for comparison.
First of all, let us understand the basic characteristics and usage of C language and C.
C language is a structured, procedural programming language developed by American computer scientist Dennis Ritchie in the 1970s. C language is widely popular for its simplicity and efficiency. It can not only be used for embedded system development, operating systems and other underlying applications, but also for application development. C is an object-oriented programming language extended from the C language and developed in the 1980s by Dennis Ritchie's colleague Bjarne Straustrup. C adds object-oriented programming features to the C language and supports concepts such as classes, inheritance, and polymorphism, making programs more reusable.
For newcomers to programming, both C language and C have their advantages and applicable scenarios. Below we will compare the advantages and disadvantages of C language and C from the following aspects, and give specific code examples to illustrate.
- Learning Curve
For novice programmers, the learning curve is a very important consideration. C language is relatively simple and has clear syntax, making it more suitable for beginners to get started quickly. C is relatively more complex, especially the object-oriented concepts that take a certain amount of time to understand and master. The following is a simple C language sample code:
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
printf("Hello, World!
");
return 0;
}The following is a C sample code, which also implements the function:
#include <iostream>
int main() {
std::cout << "Hello, World!" << std::endl;
return 0;
}As can be seen from the above example code, there are some differences in syntax between C language and C. C introduces new concepts such as namespaces, classes, templates, etc., which is relatively more complex. Therefore, for novices who have a steep learning curve and want to get started with programming quickly, it is recommended to learn C language first.
- Application fields
C language and C also have some differences in application fields. C language is more suitable for low-level development, such as operating systems, embedded systems, etc.; while C has wider applications in game development, graphics and image processing and other fields. The following is a simple C language sample code to implement the function of a calculator:
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
float num1, num2;
char op;
printf("Enter two numbers: ");
scanf("%f %f", &num1, &num2);
printf("Enter an operator ( , -, *, /): ");
scanf(" %c", &op);
float result;
switch(op) {
case ' ':
result = num1 num2;
break;
case '-':
result = num1 - num2;
break;
case '*':
result = num1 * num2;
break;
case '/':
result = num1 / num2;
break;
default:
printf("Error! Invalid operator.");
return -1;
}
printf("Result: %.2f
", result);
return 0;
}The following is a C sample code, which also implements the function of a calculator:
#include <iostream>
int main() {
float num1, num2, result;
char op;
std::cout << "Enter two numbers: ";
std::cin >> num1 >> num2;
std::cout << "Enter an operator ( , -, *, /): ";
std::cin >> op;
switch(op) {
case ' ':
result = num1 num2;
break;
case '-':
result = num1 - num2;
break;
case '*':
result = num1 * num2;
break;
case '/':
result = num1 / num2;
break;
default:
std::cout << "Error! Invalid operator." << std::endl;
return -1;
}
std::cout << "Result: " << result << std::endl;
return 0;
}As can be seen from the above sample code, when C language and C implement the same function, the output statement of C is more concise, using the stream operator provided by the iostream library.
- Objects and Classes
As an object-oriented programming language, C emphasizes the concepts of classes and objects more than C language, which makes C more flexible and extensible in programming. The following is a simple C example code that implements a simple student class and object:
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
class Student {
public:
std::string name;
int age;
void display() {
std::cout << "Name: " << name << std::endl;
std::cout << "Age: " << age << std::endl;
}
};
int main() {
Student s;
s.name = "Alice";
s.age = 20;
s.display();
return 0;
}As can be seen from the above sample code, defining classes and objects in C is more intuitive and flexible than C language, and is more convenient to use.
To sum up, C language is suitable for beginners in programming, with simple syntax and a relatively low learning curve; while C is more suitable for advanced learning, and object-oriented ideas are easier to understand and apply. Therefore, it is more important to choose whether to learn C language or C based on personal needs and learning goals. I hope the above comparison and code examples can help everyone better understand C language and C++, and choose a programming language that suits you for learning and practice.
The above is the detailed content of C Language vs. C: Which Is Better for New Programmers. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 How to calculate list length in Python?
May 23, 2025 pm 10:30 PM
How to calculate list length in Python?
May 23, 2025 pm 10:30 PM
The easiest way to calculate list length in Python is to use the len() function. 1) The len() function is suitable for lists, strings, tuples, dictionaries, etc., and returns the number of elements. 2) Although custom length calculation function is feasible, it is inefficient and is not recommended to use it in practical applications. 3) When processing large data sets, you can first calculate the length to avoid repeated calculations and improve performance. Using the len() function is simple, fast and reliable, and is the best practice for calculating list lengths.
 The difference between programming in Java and other languages ??Analysis of the advantages of cross-platform features of Java
May 20, 2025 pm 08:21 PM
The difference between programming in Java and other languages ??Analysis of the advantages of cross-platform features of Java
May 20, 2025 pm 08:21 PM
The main difference between Java and other programming languages ??is its cross-platform feature of "writing at once, running everywhere". 1. The syntax of Java is close to C, but it removes pointer operations that are prone to errors, making it suitable for large enterprise applications. 2. Compared with Python, Java has more advantages in performance and large-scale data processing. The cross-platform advantage of Java stems from the Java virtual machine (JVM), which can run the same bytecode on different platforms, simplifying development and deployment, but be careful to avoid using platform-specific APIs to maintain cross-platformity.
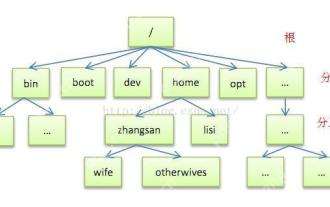 Detailed introduction to each directory of Linux and each directory (reprinted)
May 22, 2025 pm 07:54 PM
Detailed introduction to each directory of Linux and each directory (reprinted)
May 22, 2025 pm 07:54 PM
[Common Directory Description] Directory/bin stores binary executable files (ls, cat, mkdir, etc.), and common commands are generally here. /etc stores system management and configuration files/home stores all user files. The root directory of the user's home directory is the basis of the user's home directory. For example, the home directory of the user user is /home/user. You can use ~user to represent /usr to store system applications. The more important directory /usr/local Local system administrator software installation directory (install system-level applications). This is the largest directory, and almost all the applications and files to be used are in this directory. /usr/x11r6?Directory for storing x?window/usr/bin?Many
 What does u mean in c language? Unsigned modification of u in c language
May 16, 2025 pm 02:06 PM
What does u mean in c language? Unsigned modification of u in c language
May 16, 2025 pm 02:06 PM
u is used in C language to declare unsigned integer constants. 1. The u suffix represents an unsigned integer, such as 10u. 2. The range of unsigned integers starts from 0 and does not contain negative numbers. They are suitable for large-range positive numbers and bit operations. 3. Pay attention to overflow and negative number processing issues when using unsigned integers.
 How to reduce the use of global variables in C?
May 23, 2025 pm 09:03 PM
How to reduce the use of global variables in C?
May 23, 2025 pm 09:03 PM
Reducing the use of global variables in C can be achieved by: 1. Using encapsulation and singleton patterns to hide data and limit instances; 2. Using dependency injection to pass dependencies; 3. Using local static variables to replace global shared data; 4. Reduce the dependence of global variables through namespace and modular organization of code.
 c: What does it mean? Data bit c Median domain definition colon usage
May 23, 2025 pm 08:48 PM
c: What does it mean? Data bit c Median domain definition colon usage
May 23, 2025 pm 08:48 PM
In C, the bit field is a structure member that specifies the number of bits, used to save memory and directly manipulate hardware. Example: structMyStruct{inta:2;intb:5;intc:1;}. The advantage of bit domains is memory savings, but there are cross-platform issues, access restrictions and assignments that require caution. Example of usage: structStateMachine{unsignedintpower:1;unsignedintmode:2;unsignedinterror:1;}. Performance recommendations include arranging bit fields by size, avoiding overuse and adequate testing.
 Usage of ? in c Analysis of three-item operator instance in c
May 23, 2025 pm 09:09 PM
Usage of ? in c Analysis of three-item operator instance in c
May 23, 2025 pm 09:09 PM
The syntax of the trigonometric operator in C is condition?expression1:expression2, which is used to select and execute different expressions according to the condition. 1) Basic usage example: intmax=(x>y)?x:y, used to select the larger value in x and y. 2) Example of nested usage: intresult=(a>0&&b>0)?a b:(a==0||b==0)?a*b:a-b, used to perform different operations according to different conditions. 3) Error handling example: std::stringerrorMessage=(errorCode==0)?"Successful&quo
 Usage of c Typical application scenarios of logical non-operators
May 23, 2025 pm 08:42 PM
Usage of c Typical application scenarios of logical non-operators
May 23, 2025 pm 08:42 PM
The usage of logical non-operator! in C includes: 1) Basic usage: inverse the Boolean value; 2) Conditional judgment: simplify the code, such as checking whether the container is empty; 3) Loop control: processing elements that do not meet the conditions; 4) Function return value processing: determine whether the operation has failed. Pay attention to potential pitfalls such as pointer processing and operator priority when using!, but it can help write more concise and efficient code.






