 Java
Java
 javaTutorial
javaTutorial
 How does the JavaFX library attempt to address platform inconsistencies in GUI development?
How does the JavaFX library attempt to address platform inconsistencies in GUI development?
How does the JavaFX library attempt to address platform inconsistencies in GUI development?
Apr 30, 2025 am 12:01 AMJavaFX effectively addresses platform inconsistencies in GUI development by using a platform-agnostic scene graph and CSS styling. 1) It abstracts platform specifics through a scene graph, ensuring consistent rendering across Windows, macOS, and Linux. 2) CSS styling allows for fine-tuning the UI to match native looks or maintain a custom style across platforms. Despite its effectiveness, developers must be prepared to optimize for performance differences and handle platform-specific quirks.

JavaFX tackles the thorny issue of platform inconsistencies in GUI development with a finesse that's both admirable and practical. Let's dive into how it does this and explore the nuances of working with JavaFX in a multi-platform environment.
JavaFX, as a rich client platform, aims to provide a consistent user experience across different operating systems like Windows, macOS, and Linux. The core idea is to abstract away the underlying platform specifics so developers can focus on creating applications that look and feel the same everywhere. This is no small feat considering the vast differences in native UI components and behaviors across platforms.
When you're knee-deep in JavaFX development, you'll find that it uses a scene graph to manage the visual elements of your application. This scene graph is platform-agnostic, meaning it doesn't care whether it's running on Windows or macOS; it just renders the scene as defined. This abstraction layer is crucial for maintaining consistency. Here's a quick peek at how you might set up a simple scene in JavaFX:
import javafx.application.Application;
import javafx.scene.Scene;
import javafx.scene.control.Button;
import javafx.scene.layout.StackPane;
import javafx.stage.Stage;
public class SimpleSceneExample extends Application {
@Override
public void start(Stage primaryStage) {
Button btn = new Button("Click me");
StackPane root = new StackPane();
root.getChildren().add(btn);
Scene scene = new Scene(root, 300, 250);
primaryStage.setTitle("Simple Scene");
primaryStage.setScene(scene);
primaryStage.show();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
launch(args);
}
}This code snippet creates a simple window with a button, which will look and behave similarly across different platforms. The magic happens behind the scenes where JavaFX translates the scene graph into native widgets or uses its own rendering engine, Prism, to draw the UI directly.
But, let's not sugarcoat it—JavaFX isn't perfect. While it does a commendable job at providing a consistent look and feel, there are still some platform-specific quirks you might encounter. For instance, the behavior of certain controls might differ slightly, or you might need to tweak your CSS to get the exact look you want on different systems. These are the kinds of challenges that keep us developers on our toes.
From my experience, one of the key advantages of JavaFX is its ability to leverage CSS for styling. This means you can fine-tune your application's appearance to match the native look of each platform or maintain a custom style across all of them. Here's a snippet of how you might use CSS to style a button:
// In your JavaFX application
btn.setStyle("-fx-background-color: #3498db; -fx-text-fill: white;");/* In your external CSS file */
.button {
-fx-background-color: #3498db;
-fx-text-fill: white;
}This approach allows you to maintain a consistent UI while still having the flexibility to adapt to different platforms if needed.
Now, let's talk about some of the pitfalls and how to navigate them. One common issue is performance differences across platforms. JavaFX might run smoothly on one system but feel a bit sluggish on another due to hardware or driver differences. To mitigate this, always profile your application on different platforms and optimize accordingly. For instance, you might need to adjust animations or reduce the complexity of your scene graph to ensure a smooth experience everywhere.
Another aspect to consider is the integration with native system features. JavaFX provides some level of integration, like file dialogs and system notifications, but it's not as seamless as native applications. If deep system integration is crucial for your app, you might need to use platform-specific libraries or Java Native Interface (JNI) to bridge the gap.
In terms of best practices, always keep your JavaFX code modular and test-driven. This approach not only helps in maintaining a clean codebase but also makes it easier to test your application on different platforms. Use JavaFX's built-in testing tools and consider using continuous integration to run your tests on multiple platforms automatically.
To wrap up, JavaFX does an impressive job at addressing platform inconsistencies in GUI development. It provides a robust framework for creating cross-platform applications with a consistent look and feel. However, it's important to be aware of its limitations and be prepared to tweak and optimize your application to ensure the best user experience across all platforms. From my years of working with JavaFX, I can say that while it has its challenges, the rewards of creating a truly cross-platform application are well worth the effort.
The above is the detailed content of How does the JavaFX library attempt to address platform inconsistencies in GUI development?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
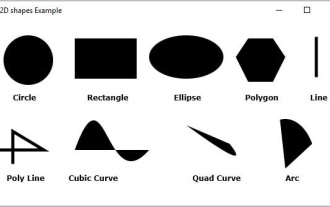 What are the various 2D shapes provided by JavaFX?
Sep 03, 2023 pm 09:41 PM
What are the various 2D shapes provided by JavaFX?
Sep 03, 2023 pm 09:41 PM
Below are the various geometric shapes you can draw using JavaFX Lines - A line is a geometric structure that connects two points. javafx.scene.shape. The Line class represents a line in the XY plane. Rectangle - A rectangle is a four-sided polygon with two pairs of parallel and concurrent sides, and all interior angles are right angles. javafx.scene. The Rectangle class represents a rectangle in the XY plane. Circle - A circle is a line forming a closed loop, with each point on it being a fixed distance from the center point. javafx.scene. The Circle class represents a circle in the XY plane. Ellipse - An ellipse is defined by two points, each point is called a focus. If you take any point on the ellipse, the sum of the distances to the focus
 Display web content using the new JavaFX WebView component in Java 13
Aug 01, 2023 pm 01:09 PM
Display web content using the new JavaFX WebView component in Java 13
Aug 01, 2023 pm 01:09 PM
Use the new JavaFXWebView component in Java13 to display web content. With the continuous development of Java, JavaFX has become one of the main tools for building cross-platform graphical interfaces. JavaFX provides a wealth of graphics libraries and components, allowing developers to easily create a variety of user interfaces. Among them, the JavaFXWebView component is a very useful component that allows us to display web content in JavaFX applications. In Java13, J
 Go Language GUI Development Guide: Implementing Cross-Platform Interface Design
Mar 22, 2024 pm 02:00 PM
Go Language GUI Development Guide: Implementing Cross-Platform Interface Design
Mar 22, 2024 pm 02:00 PM
As a fast and efficient programming language, Go language has been widely used in back-end development. However, with the continuous development of Go language, more and more developers are beginning to try to use Go language for GUI interface development in the front-end field. This article will introduce readers to how to use Go language for cross-platform GUI interface design, and provide specific code examples to help readers get started and apply it better. 1. Introduction to Go language GUI development GUI (GraphicalUserInterface, for graphics)
 Build desktop applications using Spring Boot and JavaFX
Jun 22, 2023 am 10:55 AM
Build desktop applications using Spring Boot and JavaFX
Jun 22, 2023 am 10:55 AM
As technology continues to evolve, we can now use different technologies to build desktop applications. SpringBoot and JavaFX are one of the more popular choices now. This article will focus on how to use these two frameworks to build a feature-rich desktop application. 1. Introduction to SpringBoot and JavaFXSpringBoot is a rapid development framework based on the Spring framework. It helps developers quickly build web applications while providing a set of
 Java Error: JavaFX View Error, How to Handle and Avoid
Jun 25, 2023 am 08:47 AM
Java Error: JavaFX View Error, How to Handle and Avoid
Jun 25, 2023 am 08:47 AM
JavaFX is a user interface framework for the Java platform, similar to Swing, but more modern and flexible. However, you may encounter some view errors when using it. This article will introduce how to deal with and avoid these errors. 1. Types of JavaFX view errors When using JavaFX, you may encounter the following view errors: NullPointerException This is one of the most common errors and usually occurs when trying to access an uninitialized or non-existent object. This may
 How to implement a graphical interface for real-time communication using JavaFX and WebSocket in Java 9
Jul 30, 2023 pm 04:57 PM
How to implement a graphical interface for real-time communication using JavaFX and WebSocket in Java 9
Jul 30, 2023 pm 04:57 PM
How to use JavaFX and WebSocket to implement a graphical interface for real-time communication in Java9 Introduction: With the development of the Internet, the need for real-time communication is becoming more and more common. In Java9, we can use JavaFX and WebSocket technology to implement real-time communication applications with graphical interfaces. This article will introduce how to use JavaFX and WebSocket technology to implement a graphical interface for real-time communication in Java9, and attach corresponding code examples. Part One: Ja
 Java Error: JavaFX Tag Error, How to Handle and Avoid
Jun 24, 2023 pm 11:17 PM
Java Error: JavaFX Tag Error, How to Handle and Avoid
Jun 24, 2023 pm 11:17 PM
Java is a widely used programming language, and JavaFX is a graphical interface development tool on the Java platform. However, it is inevitable to encounter the problem of JavaFX tag errors during the development process. How to deal with and avoid it? 1. Types and common causes of JavaFX tag errors: tag name errors: tag names are spelled incorrectly, capitalization is incorrect, or punctuation errors are incorrect, etc. Unclosed tags: tags must appear in pairs, with a start tag and an end tag containing their content. If the closing tag is missing from the code, it will
 How to use JavaFX to build responsive UI interfaces in Java 9
Jul 30, 2023 pm 06:36 PM
How to use JavaFX to build responsive UI interfaces in Java 9
Jul 30, 2023 pm 06:36 PM
How to use JavaFX to build a responsive UI interface in Java9 Introduction: In the development process of computer applications, the user interface (UI) is a very important part. A good UI can improve the user experience and make the application more attractive. JavaFX is a graphical user interface (GUI) framework on the Java platform. It provides a rich set of tools and APIs to quickly build interactive UI interfaces. In Java 9, JavaFX has become a JavaSE





