To manage Linux user groups, you need to master the operation of viewing, creating, deleting, modifying, and user attribute adjustment. To view user group information, you can use cat /etc/group or getent group, use groups [username] or id [username] to view the group to which the user belongs; use groupadd to create a group, and use groupdel to specify the GID; use groupdel to delete empty groups; use usermod -aG to add users to the group, and use usermod -g to modify the main group; use usermod -g to remove users from the group by editing /etc/group or using the vigr command; use groupmod -n (change name) or groupmod -g (change GID) to modify group properties, and remember to update the relevant file permissions.

Managing user groups in Linux systems is a basic but important task in system management. Whether it is adding, deleting groups, or adjusting the group permissions to which the user belongs, certain operation skills and understanding are required. Here are some practical methods and suggestions to help you better manage user groups in Linux.
View user groups in the current system
User group information in Linux is mainly stored in /etc/group file. You can directly use cat /etc/group to view all groups and their members.
The more commonly used commands are:
-
getent group: Displays all groups (including those obtained through network services such as LDAP) -
groups [用戶名]: View the group to which a user belongs -
id [用戶名]: View the user's UID, GID and group
These commands can help you quickly understand the current system's group structure and user attributes.
Create and delete user groups
Creating a new user group is very simple, just use the groupadd command:
sudo groupadd newgroup
If you want to specify a GID (group ID), you can add the -g parameter:
sudo groupadd -g 1010 newgroup
To delete an empty group (group without members) you can use groupdel :
sudo groupdel newgroup
Note: If the group has been set as the default group by a user, it cannot be deleted directly. You need to modify or delete the relevant user account first.
Add or remove a user to or from a group
To add an existing user to a group, you can use the usermod command:
sudo usermod -aG groupname username
Here -aG means "append" to the specified group without affecting the user's existing permissions for other groups.
If you just want to modify the user's primary group, you can omit -a :
sudo usermod -g groupname username
To remove a user from a group, there is no direct command, you can manually delete the user name by editing the /etc/group file, or use one of the following methods:
- Use the
vigrcommand to safely edit group files - Automate processing with scripts or tools (for batch operations)
Modify the properties of an existing group
Use the groupmod command to modify the name or GID of the group:
sudo groupmod -n newname oldname sudo groupmod -g 1020 groupname
After modifying the group name or GID, remember to check whether there are files or directories in the system that belong to the old GID and update the permissions accordingly:
find / -group oldgid -exec chgrp newgid {} \;Basically that's it. By mastering these basic commands, you can manage and maintain user groups in Linux systems well. Although it doesn't seem complicated, slight negligence may also cause permission problems, especially in environments where multiple people collaborate or multi-service operation, it is best to confirm clearly before operation.
The above is the detailed content of How to manage groups on Linux. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 Hadoop pseudo-distributed cluster construction
May 07, 2025 pm 04:45 PM
Hadoop pseudo-distributed cluster construction
May 07, 2025 pm 04:45 PM
Software preparation I am using a virtual machine with CentOS-6.6, with the host name repo. Refer to the steps to install a Linux virtual machine in Windows, I installed JDK in that virtual machine, refer to the guide to installing JDK in Linux. In addition, the virtual machine is configured with a key-free login itself, and the settings for configuring key-free login between each virtual machine are referenced. The download address of Hadoop installation package is: https://mirrors.aliyun.com/apache/hadoop/common/. I am using hadoop 2.6.5 version. Upload the Hadoop installation package to the server and unzip [root@repo~]#tarzxv
 .NET Core Quick Start Tutorial 1. The beginning: Talking about .NET Core
May 07, 2025 pm 04:54 PM
.NET Core Quick Start Tutorial 1. The beginning: Talking about .NET Core
May 07, 2025 pm 04:54 PM
1. The Origin of .NETCore When talking about .NETCore, we must not mention its predecessor .NET. Java was in the limelight at that time, and Microsoft also favored Java. The Java virtual machine on the Windows platform was developed by Microsoft based on JVM standards. It is said to be the best performance Java virtual machine at that time. However, Microsoft has its own little abacus, trying to bundle Java with the Windows platform and add some Windows-specific features. Sun's dissatisfaction with this led to a breakdown of the relationship between the two parties, and Microsoft then launched .NET. .NET has borrowed many features of Java since its inception and gradually surpassed Java in language features and form development. Java in version 1.6
 Postman Integrated Application on CentOS
May 19, 2025 pm 08:00 PM
Postman Integrated Application on CentOS
May 19, 2025 pm 08:00 PM
Integrating Postman applications on CentOS can be achieved through a variety of methods. The following are the detailed steps and suggestions: Install Postman by downloading the installation package to download Postman's Linux version installation package: Visit Postman's official website and select the version suitable for Linux to download. Unzip the installation package: Use the following command to unzip the installation package to the specified directory, for example /opt: sudotar-xzfpostman-linux-x64-xx.xx.xx.tar.gz-C/opt Please note that "postman-linux-x64-xx.xx.xx.tar.gz" is replaced by the file name you actually downloaded. Create symbols
 The difference between programming in Java and other languages ??Analysis of the advantages of cross-platform features of Java
May 20, 2025 pm 08:21 PM
The difference between programming in Java and other languages ??Analysis of the advantages of cross-platform features of Java
May 20, 2025 pm 08:21 PM
The main difference between Java and other programming languages ??is its cross-platform feature of "writing at once, running everywhere". 1. The syntax of Java is close to C, but it removes pointer operations that are prone to errors, making it suitable for large enterprise applications. 2. Compared with Python, Java has more advantages in performance and large-scale data processing. The cross-platform advantage of Java stems from the Java virtual machine (JVM), which can run the same bytecode on different platforms, simplifying development and deployment, but be careful to avoid using platform-specific APIs to maintain cross-platformity.
 Where is the pycharm interpreter?
May 23, 2025 pm 10:09 PM
Where is the pycharm interpreter?
May 23, 2025 pm 10:09 PM
Setting the location of the interpreter in PyCharm can be achieved through the following steps: 1. Open PyCharm, click the "File" menu, and select "Settings" or "Preferences". 2. Find and click "Project:[Your Project Name]" and select "PythonInterpreter". 3. Click "AddInterpreter", select "SystemInterpreter", browse to the Python installation directory, select the Python executable file, and click "OK". When setting up the interpreter, you need to pay attention to path correctness, version compatibility and the use of the virtual environment to ensure the smooth operation of the project.
 How to manually install plugin packages in VSCode
May 15, 2025 pm 09:33 PM
How to manually install plugin packages in VSCode
May 15, 2025 pm 09:33 PM
The steps to manually install the plug-in package in VSCode are: 1. Download the .vsix file of the plug-in; 2. Open VSCode and press Ctrl Shift P (Windows/Linux) or Cmd Shift P (Mac) to call up the command panel; 3. Enter and select Extensions:InstallfromVSIX..., then select .vsix file and install. Manually installing plug-ins provides a flexible way to install, especially when the network is restricted or the plug-in market is unavailable, but attention needs to be paid to file security and possible dependencies.
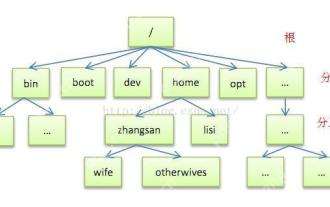 Detailed introduction to each directory of Linux and each directory (reprinted)
May 22, 2025 pm 07:54 PM
Detailed introduction to each directory of Linux and each directory (reprinted)
May 22, 2025 pm 07:54 PM
[Common Directory Description] Directory/bin stores binary executable files (ls, cat, mkdir, etc.), and common commands are generally here. /etc stores system management and configuration files/home stores all user files. The root directory of the user's home directory is the basis of the user's home directory. For example, the home directory of the user user is /home/user. You can use ~user to represent /usr to store system applications. The more important directory /usr/local Local system administrator software installation directory (install system-level applications). This is the largest directory, and almost all the applications and files to be used are in this directory. /usr/x11r6?Directory for storing x?window/usr/bin?Many
 After installing Nginx, the configuration file path and initial settings
May 16, 2025 pm 10:54 PM
After installing Nginx, the configuration file path and initial settings
May 16, 2025 pm 10:54 PM
Understanding Nginx's configuration file path and initial settings is very important because it is the first step in optimizing and managing a web server. 1) The configuration file path is usually /etc/nginx/nginx.conf. The syntax can be found and tested using the nginx-t command. 2) The initial settings include global settings (such as user, worker_processes) and HTTP settings (such as include, log_format). These settings allow customization and extension according to requirements. Incorrect configuration may lead to performance issues and security vulnerabilities.






