JDBC Basics Introduction
Concept
JDBC (Java DataBase Connectivity, java database connection) is a Java API used to execute SQL statements, which can provide unification for a variety of relational databases Access, which consists of a set of classes and interfaces written in Java language.
??The JDBC specification defines the interface, and the specific implementation is implemented by major database vendors.
A specific database driver implementation is required to operate the database in Java, because JDBC is only the standard specification for Java to access the database. Each database vendor writes its own database driver based on the communication format of its database. Therefore, you only need to master the invocation of JDBC interface methods, and the database manufacturer will provide a database driver.
Essence
is actually a set of specifications (interfaces) officially provided by java. Used to help developers quickly connect different relational databases!
7 steps of JDBC
(1) Import jar package
(2) Register driver
Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver"); Note: If you use a higher version of MySQL, you must use the com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver method, otherwise an error will be reported!
Loading class `com.mysql.jdbc.Driver'. This is deprecated. The new driver class is `com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver'. The driver is automatically registered via the SPI and manual loading of the driver class is generally unnecessary.
If it is a lower version, you can use com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
If you still get an error, You can add the time zone to the url!
url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/Database name?serverTimezone=UTC
(3) Get the connection
String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/db1"; Connection con = DriverManager.getConnection(url,"root","888888");
(4) Get the executor object
Statement stat = con.createStatement();
(5) Execute the sql statement and receive the return result
String sql = "SELECT * FROM user"; ResultSet rs = stat.executeQuery(sql);
(6) Processing results
while(rs.next()) {
System.out.println( rs.getInt("id")
+ "\t" + rs.getString("name"));
}(7) Release resources
con.close(); stat.close(); rs.close();
JDBC entry sample code
Change the user name, database name, and password in the Connection object to your own!
public class jdbc_demo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException, SQLException {
// 1.導(dǎo)入jar包
// 2.注冊(cè)驅(qū)動(dòng)
Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver");
// 3.獲取連接
String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/db1";
Connection con = DriverManager.getConnection(url,"root","888888");
// 4.獲取執(zhí)行者對(duì)象
Statement stat = con.createStatement();
// 5.執(zhí)行sql語句,并且接收結(jié)果
String sql = "SELECT * FROM product";
ResultSet rs = stat.executeQuery(sql);
// 6.處理結(jié)果
while(rs.next()) {
System.out.println( rs.getInt("id") + "\t"
+ rs.getString("name") + "\t"
+ rs.getInt("price") + "\t"
+ rs.getString("brand") + "\t"
+ rs.getInt("stock")
);
}
// 7。釋放資源
con.close();
stat.close();
rs.close();
}
}The results are as follows:
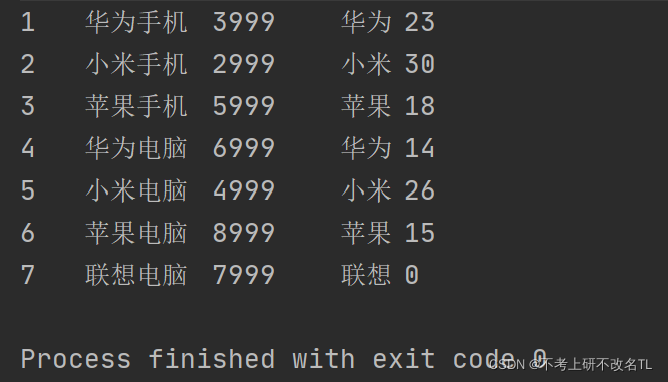
The above is the detailed content of How MySQL implements JDBC. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 What are the transaction isolation levels in MySQL, and which is the default?
Jun 23, 2025 pm 03:05 PM
What are the transaction isolation levels in MySQL, and which is the default?
Jun 23, 2025 pm 03:05 PM
MySQL's default transaction isolation level is RepeatableRead, which prevents dirty reads and non-repeatable reads through MVCC and gap locks, and avoids phantom reading in most cases; other major levels include read uncommitted (ReadUncommitted), allowing dirty reads but the fastest performance, 1. Read Committed (ReadCommitted) ensures that the submitted data is read but may encounter non-repeatable reads and phantom readings, 2. RepeatableRead default level ensures that multiple reads within the transaction are consistent, 3. Serialization (Serializable) the highest level, prevents other transactions from modifying data through locks, ensuring data integrity but sacrificing performance;
 How to add the MySQL bin directory to the system PATH
Jul 01, 2025 am 01:39 AM
How to add the MySQL bin directory to the system PATH
Jul 01, 2025 am 01:39 AM
To add MySQL's bin directory to the system PATH, it needs to be configured according to the different operating systems. 1. Windows system: Find the bin folder in the MySQL installation directory (the default path is usually C:\ProgramFiles\MySQL\MySQLServerX.X\bin), right-click "This Computer" → "Properties" → "Advanced System Settings" → "Environment Variables", select Path in "System Variables" and edit it, add the MySQLbin path, save it and restart the command prompt and enter mysql--version verification; 2.macOS and Linux systems: Bash users edit ~/.bashrc or ~/.bash_
 How to install MySQL on Windows 11
Jun 29, 2025 am 01:47 AM
How to install MySQL on Windows 11
Jun 29, 2025 am 01:47 AM
The key steps for installing MySQL on Windows 11 are as follows: 1. Download the correct version, select the Windows MSI installation package and ensure that the system is 64-bit; 2. Select the "Custom" mode during installation, add MySQLServer and set the appropriate installation path; 3. Run the configuration wizard, select the "ServerComputer" configuration type, set the root password, and select the automatic startup method; 4. After the test installation is successful, if the prompt command is unavailable, add the MySQL bin directory to the system PATH environment variable. Follow these steps to complete the installation and configuration smoothly.
 Resetting the root password for MySQL server
Jul 03, 2025 am 02:32 AM
Resetting the root password for MySQL server
Jul 03, 2025 am 02:32 AM
To reset the root password of MySQL, please follow the following steps: 1. Stop the MySQL server, use sudosystemctlstopmysql or sudosystemctlstopmysqld; 2. Start MySQL in --skip-grant-tables mode, execute sudomysqld-skip-grant-tables&; 3. Log in to MySQL and execute the corresponding SQL command to modify the password according to the version, such as FLUSHPRIVILEGES;ALTERUSER'root'@'localhost'IDENTIFIEDBY'your_new
 Handling NULL Values in MySQL Columns and Queries
Jul 05, 2025 am 02:46 AM
Handling NULL Values in MySQL Columns and Queries
Jul 05, 2025 am 02:46 AM
When handling NULL values ??in MySQL, please note: 1. When designing the table, the key fields are set to NOTNULL, and optional fields are allowed NULL; 2. ISNULL or ISNOTNULL must be used with = or !=; 3. IFNULL or COALESCE functions can be used to replace the display default values; 4. Be cautious when using NULL values ??directly when inserting or updating, and pay attention to the data source and ORM framework processing methods. NULL represents an unknown value and does not equal any value, including itself. Therefore, be careful when querying, counting, and connecting tables to avoid missing data or logical errors. Rational use of functions and constraints can effectively reduce interference caused by NULL.
 Troubleshooting MySQL installation errors on Windows
Jun 27, 2025 am 01:22 AM
Troubleshooting MySQL installation errors on Windows
Jun 27, 2025 am 01:22 AM
Common problems with installing MySQL on Windows include the service cannot be started, the port is occupied or the configuration failed. The solutions are as follows: 1. When encountering "MySQL80 service cannot be started", you should stop and delete the old service, clean up residual data, or use the "Remove" function that comes with the installer; 2. If an error is reported as "Error:1053" when starting the service, you need to check the log to confirm the port conflict and modify the port number in my.ini; 3. When the configuration wizard prompts "Service not responding", check and end the unresponsive mysqld.exe process, or manually run mysqld--console to view the output; 4. If the connection to the database is denied, you can use the password-free login method to reset the root user password.
 Analyzing the MySQL Slow Query Log to Find Performance Bottlenecks
Jul 04, 2025 am 02:46 AM
Analyzing the MySQL Slow Query Log to Find Performance Bottlenecks
Jul 04, 2025 am 02:46 AM
Turn on MySQL slow query logs and analyze locationable performance issues. 1. Edit the configuration file or dynamically set slow_query_log and long_query_time; 2. The log contains key fields such as Query_time, Lock_time, Rows_examined to assist in judging efficiency bottlenecks; 3. Use mysqldumpslow or pt-query-digest tools to efficiently analyze logs; 4. Optimization suggestions include adding indexes, avoiding SELECT*, splitting complex queries, etc. For example, adding an index to user_id can significantly reduce the number of scanned rows and improve query efficiency.
 Performing logical backups using mysqldump in MySQL
Jul 06, 2025 am 02:55 AM
Performing logical backups using mysqldump in MySQL
Jul 06, 2025 am 02:55 AM
mysqldump is a common tool for performing logical backups of MySQL databases. It generates SQL files containing CREATE and INSERT statements to rebuild the database. 1. It does not back up the original file, but converts the database structure and content into portable SQL commands; 2. It is suitable for small databases or selective recovery, and is not suitable for fast recovery of TB-level data; 3. Common options include --single-transaction, --databases, --all-databases, --routines, etc.; 4. Use mysql command to import during recovery, and can turn off foreign key checks to improve speed; 5. It is recommended to test backup regularly, use compression, and automatic adjustment.






