HTML Style Attribute
Sep 04, 2024 pm 04:18 PMHTML code needs the style attribute for web pages rendered in web browsers like Chrome, Firefox, and IE to be displayed as they are intended to look. HTML tags can contain various information, and the style attribute controls the appearance of information in HTML blocks using inline styling.
This article will learn more about the HTML style attribute, which is nothing more than a set of rules defining how a page will be rendered in the web browser.
List of HTML Style Attributes
Here’s a list of all the style properties that can be used to influence and control the design of HTML elements, accompanied by a practical example :
1. Background-Color
This CSS property allows us to?set the background color for any HTML element like
, etc.
Example
<div style="background-color:blue">My background is blue</div>
Output:

2. Color
The font color of the text in an HTML element can be controlled by setting its color attribute to the right color name, HEX?code, or RGB code.
Example
<div style="color:blue">My font color is blue</div>
Output:

3. Border Color
We can set the border color of any HTML element if we’d like to add a border to it.
Example
<p style="border: 1px solid red">My border is red</p>
Output:

As the code above shows, the border property accepts three properties in the following order: “Border-width border-style border-color.”
4. Background-Image
We can also set an image as a background by using the background-image property as follows:
Example:
<div style="background-image: url('https://www.google.com/images/branding/googlelogo/2x/googlelogo_color_272x92dp.png');height :365px">
Output:

5. Background-Repeat
As you see in the above example, when an image is set as background using the background-image property, it, by default, repeats the image both horizontally as well as vertically. However, some images may need to be repeated either vertically or horizontally, or they may not be needed to be repeated. This behavior can be controlled by setting the desired value against the property of background-repeat, and it can be only used when background-image is being used; else, it won’t add any styling value when used as a standalone property.
The value “repeat-x” allows the image to be repeated only horizontally.
The value “repeat-y” allows the image to be repeated only vertically.
The value “no-repeat” is used to stop any repetition of the background image.
Let us modify the above example to improve the background image.
Example?
<div style="background-image: url('https://www.google.com/images/branding/googlelogo/2x/googlelogo_color_272x92dp.png');height :365px; background-repeat:no-repeat">
Output:

We can compare the examples above and understand that with a background image; we can add an image as the background, and with a background repeat, we can control the repetition of the background image.
6. Background-Position
With this property, we can define the position of the background image.
Example
<div style="background-image: url('https://www.google.com/images/branding/googlelogo/2x/googlelogo_color_272x92dp.png');height :365px; width:500px;background-repeat: no-repeat; background-position: left bottom;">
</div>
Output:

7. Margins
CSS provides us with properties to set margins on all four sides of an HTML element, or we could add margins to a particular side of the element.
With margin-top can add a margin to the top of the element, margin-right will add a margin to the right of the element, margin-left will add a margin to the left of the element, and margin-bottom will add a margin to the bottom. Instead of using these four properties, we can also use the margin property and set its values as per our requirements.
Example
p?{
margin-top:?25px;
margin-bottom:?75px;
margin-right:?50px;
margin-left:?100px;
}
or
p
{
margin:?25px 50px 75px 100px;
}
8. Padding
The padding property defines the space between the content of an element and its borders. We can use the “padding” property or individual padding properties like padding-top, padding-bottom, padding-left, and padding-right to set the padding for the top, bottom, left, or right of the content of an element.
p {
padding-top: 25px;
padding-bottom: 75px;
padding-right: 50px;
padding-left: 100px;
}
or
p
{
padding:?25px 50px 75px 100px;
}
9. Height and Width
The most basic CSS properties used to define the height and width of any HTML element are height and width. You can set them to a pixel value, such as 200px, or a percentage, such as 10%, 20%, etc.
10. Text-Align
You can use this property to set the horizontal direction for text alignment in an element. The value options are center, right, or left.
p {
text-align: center;
}
or
p {
text-align: left;
}
or
p {
text-align: right;
}
11. Text-Decoration
Text decoration property can be used to set decorations like underline, line-through, or overline over text in HTML.
Example:
<p style="text-decoration:underline">This is underline</p>
Output:

12. Letter-Spacing
As the name suggests, this property defines the spacing between letters/characters in a word. You can assign a positive or negative pixel value to increase or decrease the spacing between letters.
Example:
<p style="letter-spacing: -3px">My words are overlapped </p>
Output:

13. Line-Height
Line height defines the distance between vertical lines. You can set the line height to a positive or negative pixel value, similar to letter spacing. Let’s review the example below to understand better:
Example:
<p style="line-height: 0.7px">This paragraph has a small line-height.<br>This paragraph has a small line-height.<br> </p>
Output:
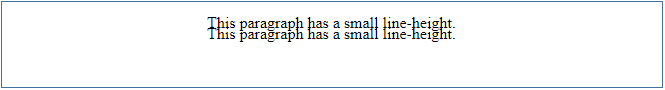
14. Text Direction
Sometimes, if the web page’s content is not in English but in some other language like Arabic, which follows a right to the left convention, we would need to change the direction of the text. In such cases, we can reverse the text direction.
Example:
<p style="direction: rtl"><bdo dir="ltr">I am right to left</bdo></p>
Output:
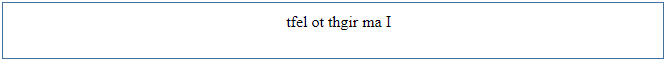
15. Text Shadow
This property adds a shadow to the text.
Example:
<p style="text-shadow: 3px 2px gray;"> I’ve got a gray shadow</p>
Output:

16. Font Family
We can define the font class for text in an element. We can define multiple font families separated by a comma as a fallback system to handle scenarios where a preferred font class cannot be loaded.
- Font style: We can add italic or oblique effects to the text with the font-style property.
Example:
<p style="font-style: oblique">This is oblique style.</p>
Output:

- Font weight: This property defines the weight of a font.
Example:
<p style="font-weight: 900"> This is a bold paragraph</p>
Output :

The styling attributes showcased above are our building blocks with UI and UX designing. New versions of CSS continue to evolve.
The above is the detailed content of HTML Style Attribute. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 What are the essential HTML elements for structuring a webpage?
Jul 03, 2025 am 02:34 AM
What are the essential HTML elements for structuring a webpage?
Jul 03, 2025 am 02:34 AM
The web page structure needs to be supported by core HTML elements. 1. The overall structure of the page is composed of , , which is the root element, which stores meta information and displays the content; 2. The content organization relies on title (-), paragraph () and block tags (such as ,) to improve organizational structure and SEO; 3. Navigation is implemented through and implemented, commonly used organizations are linked and supplemented with aria-current attribute to enhance accessibility; 4. Form interaction involves , , and , to ensure the complete user input and submission functions. Proper use of these elements can improve page clarity, maintenance and search engine optimization.
 Handling reconnections and errors with HTML5 Server-Sent Events.
Jul 03, 2025 am 02:28 AM
Handling reconnections and errors with HTML5 Server-Sent Events.
Jul 03, 2025 am 02:28 AM
When using HTML5SSE, the methods to deal with reconnection and errors include: 1. Understand the default reconnection mechanism. EventSource retrys 3 seconds after the connection is interrupted by default. You can customize the interval through the retry field; 2. Listen to the error event to deal with connection failure or parsing errors, distinguish error types and execute corresponding logic, such as network problems relying on automatic reconnection, server errors manually delay reconnection, and authentication failure refresh token; 3. Actively control the reconnection logic, such as manually closing and rebuilding the connection, setting the maximum number of retry times, combining navigator.onLine to judge network status to optimize the retry strategy. These measures can improve application stability and user experience.
 Declaring the correct HTML5 doctype for modern pages.
Jul 03, 2025 am 02:35 AM
Declaring the correct HTML5 doctype for modern pages.
Jul 03, 2025 am 02:35 AM
Doctype is a statement that tells the browser which HTML standard to use to parse the page. Modern web pages only need to be written at the beginning of the HTML file. Its function is to ensure that the browser renders the page in standard mode rather than weird mode, and must be located on the first line, with no spaces or comments in front of it; there is only one correct way to write it, and it is not recommended to use old versions or other variants; other such as charset, viewport, etc. should be placed in part.
 Implementing client-side form validation using HTML attributes.
Jul 03, 2025 am 02:31 AM
Implementing client-side form validation using HTML attributes.
Jul 03, 2025 am 02:31 AM
Client-sideformvalidationcanbedonewithoutJavaScriptbyusingHTMLattributes.1)Userequiredtoenforcemandatoryfields.2)ValidateemailsandURLswithtypeattributeslikeemailorurl,orusepatternwithregexforcustomformats.3)Limitvaluesusingmin,max,minlength,andmaxlen
 Improving SEO with HTML5 semantic markup and Microdata.
Jul 03, 2025 am 01:16 AM
Improving SEO with HTML5 semantic markup and Microdata.
Jul 03, 2025 am 01:16 AM
Using HTML5 semantic tags and Microdata can improve SEO because it helps search engines better understand page structure and content meaning. 1. Use HTML5 semantic tags such as,,,, and to clarify the function of page blocks, which helps search engines establish a more accurate page model; 2. Add Microdata structured data to mark specific content, such as article author, release date, product price, etc., so that search engines can identify information types and use them for display of rich media summary; 3. Pay attention to the correct use of tags to avoid confusion, avoid duplicate tags, test the effectiveness of structured data, regularly update to adapt to changes in schema.org, and combine with other SEO means to optimize for long-term.
 How to group options within a select dropdown using html?
Jul 04, 2025 am 03:16 AM
How to group options within a select dropdown using html?
Jul 04, 2025 am 03:16 AM
Use tags in HTML to group options in the drop-down menu. The specific method is to wrap a group of elements and define the group name through the label attribute, such as: 1. Contains options such as apples, bananas, oranges, etc.; 2. Contains options such as carrots, broccoli, etc.; 3. Each is an independent group, and the options within the group are automatically indented. Notes include: ① No nesting is supported; ② The entire group can be disabled through the disabled attribute; ③ The style is restricted and needs to be beautified in combination with CSS or third-party libraries; plug-ins such as Select2 can be used to enhance functions.
 Implementing Clickable Buttons Using the HTML button Element
Jul 07, 2025 am 02:31 AM
Implementing Clickable Buttons Using the HTML button Element
Jul 07, 2025 am 02:31 AM
To use HTML button elements to achieve clickable buttons, you must first master its basic usage and common precautions. 1. Create buttons with tags and define behaviors through type attributes (such as button, submit, reset), which is submitted by default; 2. Add interactive functions through JavaScript, which can be written inline or bind event listeners through ID to improve maintenance; 3. Use CSS to customize styles, including background color, border, rounded corners and hover/active status effects to enhance user experience; 4. Pay attention to common problems: make sure that the disabled attribute is not enabled, JS events are correctly bound, layout occlusion, and use the help of developer tools to troubleshoot exceptions. Master this
 Integrating CSS and JavaScript effectively with HTML5 structure.
Jul 12, 2025 am 03:01 AM
Integrating CSS and JavaScript effectively with HTML5 structure.
Jul 12, 2025 am 03:01 AM
HTML5, CSS and JavaScript should be efficiently combined with semantic tags, reasonable loading order and decoupling design. 1. Use HTML5 semantic tags, such as improving structural clarity and maintainability, which is conducive to SEO and barrier-free access; 2. CSS should be placed in, use external files and split by module to avoid inline styles and delayed loading problems; 3. JavaScript is recommended to be introduced in front, and use defer or async to load asynchronously to avoid blocking rendering; 4. Reduce strong dependence between the three, drive behavior through data-* attributes and class name control status, and improve collaboration efficiency through unified naming specifications. These methods can effectively optimize page performance and collaborate with teams.






