In JavaScript we have different ways to handle asynchronous calls.
It allows you to handle asynchronous tasks like fetching data from a server, reading files, or waiting for an event.
Callbacks
This is a function that calls to another function.
Let's see an example so we can understand it better:
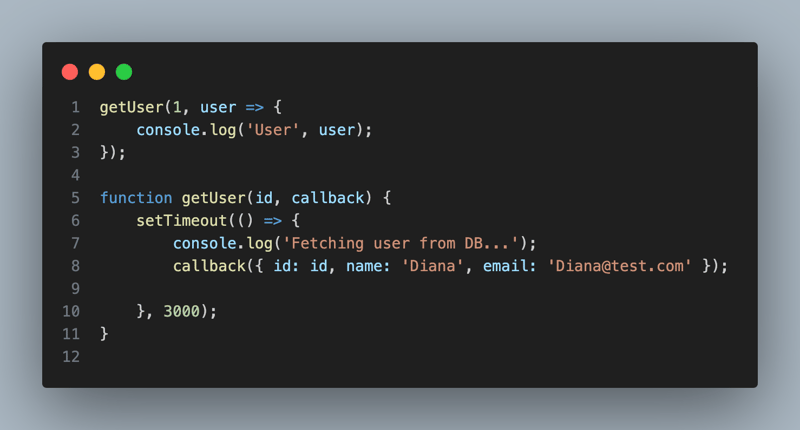
- Calling getUser() with an id and callback function that will print users id, name and email. The callback will be executed once the asynchronous getUser operation completes.
The getUser() Function:
id: This is the id of the user you want to retrieve passed from the getUser(1, ...) call.
callback: This is the function that will be called after the "user data" is retrieved (simulated here by the setTimeout() function).
Inside the setTimeout() function the callback() function is called after the delay, passing a mock user object as its argument: { id: id, name: 'Diana', email: 'Diana@test.com' }.
Execution Flow:
- getUser(1, user => { console.log('User', user); }); is called.
- Inside getUser(), a 3-second delay is triggered using setTimeout().
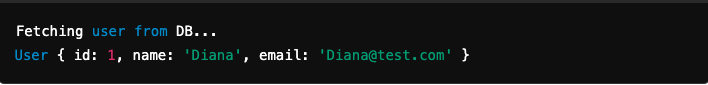
- After 3 seconds: The message 'Fetching user from DB...' is logged to the console. The callback function is invoked with the user object { id: 1, name: 'Diana', email: 'Diana@test.com' }.
- The callback function logs User and the user object to the console.
Final Output:
Callback Hell
Callback hell pattern - this happens when multiple asynchronous operations depend on each other, leading to deeply nested callbacks. As the nesting increases, the code becomes harder to read, maintain, and debug. Let's see an example:

Let's break it down:
- Fetching the User: Here, we initiate the first asynchronous call, getUser(1), which simulates fetching user data from a database. Once the data is fetched, the callback function is executed, logging the user details to the console.
getUser(1, user => {
console.log('User', user);
// ...
});
Fetching the User's Orders:
Inside the callback for getUser(), we make another asynchronous call to getOrders(user.id), simulating fetching the user's orders from the database. This requires nesting another callback inside the first one. Once the orders are fetched, the orders are logged.
getUser(1, user => {
console.log('User', user);
// ...
});
- Fetching the Order Details: After fetching the orders, we need to get the details of one specific order (orders[1]). This leads to a third level of nesting, where getOrdersDetails() is called to fetch the order details, and then logs them to the console.
getOrders(user.id, orders => {
console.log(`${user.name}'s orders`, orders);
// ...
});
Code Structure (Nesting):

Notice how each asynchronous operation depends on the previous one, resulting in a deeply nested structure. Making the code difficult to:
Read: It’s hard to follow the flow of the logic when callbacks are deeply nested.
Error handling: It's difficult to handle errors at multiple levels of callbacks.
3.Debug: Identifying where an error occurs becomes more complex when many levels of callbacks are involved.
Also it makes the code "Tight coupling" - each function depends on the previous one’s output, which means that the code is tightly coupled, reducing reusability.
Result:
Avoiding Callback Hell:
Callback hell can be avoided by using modern JavaScript features like Promises and async/await. These methods allow asynchronous code to be written in a more readable, sequential manner.
The above is the detailed content of Callbacks. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 Java vs. JavaScript: Clearing Up the Confusion
Jun 20, 2025 am 12:27 AM
Java vs. JavaScript: Clearing Up the Confusion
Jun 20, 2025 am 12:27 AM
Java and JavaScript are different programming languages, each suitable for different application scenarios. Java is used for large enterprise and mobile application development, while JavaScript is mainly used for web page development.
 Javascript Comments: short explanation
Jun 19, 2025 am 12:40 AM
Javascript Comments: short explanation
Jun 19, 2025 am 12:40 AM
JavaScriptcommentsareessentialformaintaining,reading,andguidingcodeexecution.1)Single-linecommentsareusedforquickexplanations.2)Multi-linecommentsexplaincomplexlogicorprovidedetaileddocumentation.3)Inlinecommentsclarifyspecificpartsofcode.Bestpractic
 How to work with dates and times in js?
Jul 01, 2025 am 01:27 AM
How to work with dates and times in js?
Jul 01, 2025 am 01:27 AM
The following points should be noted when processing dates and time in JavaScript: 1. There are many ways to create Date objects. It is recommended to use ISO format strings to ensure compatibility; 2. Get and set time information can be obtained and set methods, and note that the month starts from 0; 3. Manually formatting dates requires strings, and third-party libraries can also be used; 4. It is recommended to use libraries that support time zones, such as Luxon. Mastering these key points can effectively avoid common mistakes.
 Why should you place tags at the bottom of the ?
Jul 02, 2025 am 01:22 AM
Why should you place tags at the bottom of the ?
Jul 02, 2025 am 01:22 AM
PlacingtagsatthebottomofablogpostorwebpageservespracticalpurposesforSEO,userexperience,anddesign.1.IthelpswithSEObyallowingsearchenginestoaccesskeyword-relevanttagswithoutclutteringthemaincontent.2.Itimprovesuserexperiencebykeepingthefocusonthearticl
 JavaScript vs. Java: A Comprehensive Comparison for Developers
Jun 20, 2025 am 12:21 AM
JavaScript vs. Java: A Comprehensive Comparison for Developers
Jun 20, 2025 am 12:21 AM
JavaScriptispreferredforwebdevelopment,whileJavaisbetterforlarge-scalebackendsystemsandAndroidapps.1)JavaScriptexcelsincreatinginteractivewebexperienceswithitsdynamicnatureandDOMmanipulation.2)Javaoffersstrongtypingandobject-orientedfeatures,idealfor
 JavaScript: Exploring Data Types for Efficient Coding
Jun 20, 2025 am 12:46 AM
JavaScript: Exploring Data Types for Efficient Coding
Jun 20, 2025 am 12:46 AM
JavaScripthassevenfundamentaldatatypes:number,string,boolean,undefined,null,object,andsymbol.1)Numbersuseadouble-precisionformat,usefulforwidevaluerangesbutbecautiouswithfloating-pointarithmetic.2)Stringsareimmutable,useefficientconcatenationmethodsf
 What is event bubbling and capturing in the DOM?
Jul 02, 2025 am 01:19 AM
What is event bubbling and capturing in the DOM?
Jul 02, 2025 am 01:19 AM
Event capture and bubble are two stages of event propagation in DOM. Capture is from the top layer to the target element, and bubble is from the target element to the top layer. 1. Event capture is implemented by setting the useCapture parameter of addEventListener to true; 2. Event bubble is the default behavior, useCapture is set to false or omitted; 3. Event propagation can be used to prevent event propagation; 4. Event bubbling supports event delegation to improve dynamic content processing efficiency; 5. Capture can be used to intercept events in advance, such as logging or error processing. Understanding these two phases helps to accurately control the timing and how JavaScript responds to user operations.
 What's the Difference Between Java and JavaScript?
Jun 17, 2025 am 09:17 AM
What's the Difference Between Java and JavaScript?
Jun 17, 2025 am 09:17 AM
Java and JavaScript are different programming languages. 1.Java is a statically typed and compiled language, suitable for enterprise applications and large systems. 2. JavaScript is a dynamic type and interpreted language, mainly used for web interaction and front-end development.






