As frontend developers, our role extends beyond writing efficient code—we are also responsible for crafting interfaces that are intuitive and delightful for users. Understanding the fundamental laws of UX/UI empowers us to make better design decisions. Let’s explore the most important principles that shape how users interact with interfaces.
The Aesthetic-Usability Effect: Beauty Matters
First impressions are crucial. This law states that visually appealing interfaces generate greater trust and satisfaction among users. A cluttered or unattractive design can immediately cause rejection, increasing the perception of issues or insecurity, regardless of how functional the application is.
Example: Compare the original version of Facebook with its current interface. The evolution towards a cleaner and more aesthetic design has been instrumental to its success.
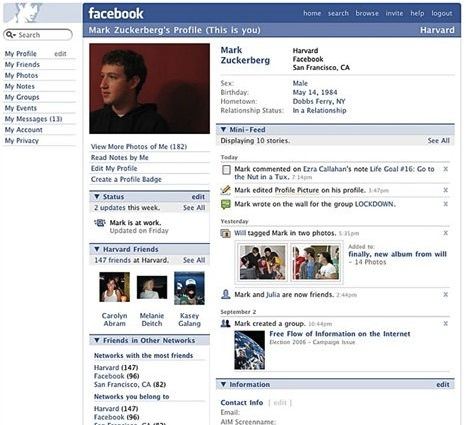

To effectively implement this law, focus on four pillars:
- Simplicity: Eliminate unnecessary elements.
- Harmony: Maintain visual balance.
- Clarity: Ensure every element has a clear purpose.
- Consistency: Keep design coherent throughout the interface.
The Zeigarnik Effect: The Power of the Unfinished
Have you ever noticed how a progress bar keeps you engaged until it reaches 100%? This is no coincidence. The Zeigarnik effect explains why users remember incomplete tasks better than completed ones.
Example: LinkedIn uses a "profile completion" progress bar that displays progress and suggests specific actions to complete the profile, keeping users engaged and encouraging them to provide as much information as possible.

As developers, we can leverage this psychological principle in various ways:
- Progress Indicators: Implement progress bars and checkpoints.
- Reward Systems: Create small victories that motivate users to continue.
- Smart Reminders: Help users resume incomplete tasks.
- Anticipation: Generate curiosity about the next steps.
Tesler’s Law: Managing Complexity
Also known as the "law of constant complexity," it teaches us that every application has an inherent amount of complexity that cannot be eliminated—only redistributed between the system and the user.
Example: Google Maps manages enormous backend complexity (routing algorithms, real-time traffic data) while presenting a simple interface to users, who only need to input their destination.

Key considerations:
- Identify unavoidable complexity in your systems.
- Take on as much complexity as possible during development.
- Avoid oversimplification that leads to confusing abstractions.
Hick’s Law: Less Is More
The time it takes to make a decision increases with the number of available options.

Example: Netflix initially displays a limited number of titles organized by categories, rather than overwhelming users with its entire catalog.

To apply it effectively:
- Reduce the number of options where possible.
- Organize options into logical categories.
- Prioritize the most important actions.
- Simplify the interface without sacrificing essential functionality.
Miller’s Law: The Magical Limit of 7±2
Our brains have limits, and this law quantifies them: we can handle approximately seven (plus or minus two) items in our short-term memory.
Example: Successful websites like Amazon organize their main navigation categories into manageable groups, using submenus for additional options.

To stay within these limits:
- Group related information.
- Limit the number of items per view.
- Implement effective search and filtering tools.
- Use pagination when necessary.
Jakob’s Law: Don’t Reinvent the Wheel
Users prefer familiarity. This law reminds us that we don’t always need to innovate in every aspect of design.
Example: The hamburger icon (?) for mobile menus has become a standard that users instantly recognize.

Best practices:
- Stick to established design patterns.
- Use conventions familiar to your users.
- Innovate only when it adds real value.
- Maintain consistency with popular websites.
Conclusion
These UX/UI laws are not just theories—they are proven principles that can make the difference between an interface users love and one they abandon in frustration. As frontend developers, integrating these principles into our development process helps create experiences that are more intuitive, enjoyable, and effective.
Remember: a great frontend doesn’t just work well—it feels good to use.
Additional Resources
- Laws of UX is a collection of best practices that designers can consider when building user interfaces.
- Miller, G. A. (1956). "The Magical Number Seven, Plus or Minus Two: Some Limits on Our Capacity for Processing Information." Psychological Review, 63(2), 81–97.
The above is the detailed content of UX/UI Laws Every Frontend Developer Should Know. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 Java vs. JavaScript: Clearing Up the Confusion
Jun 20, 2025 am 12:27 AM
Java vs. JavaScript: Clearing Up the Confusion
Jun 20, 2025 am 12:27 AM
Java and JavaScript are different programming languages, each suitable for different application scenarios. Java is used for large enterprise and mobile application development, while JavaScript is mainly used for web page development.
 Javascript Comments: short explanation
Jun 19, 2025 am 12:40 AM
Javascript Comments: short explanation
Jun 19, 2025 am 12:40 AM
JavaScriptcommentsareessentialformaintaining,reading,andguidingcodeexecution.1)Single-linecommentsareusedforquickexplanations.2)Multi-linecommentsexplaincomplexlogicorprovidedetaileddocumentation.3)Inlinecommentsclarifyspecificpartsofcode.Bestpractic
 How to work with dates and times in js?
Jul 01, 2025 am 01:27 AM
How to work with dates and times in js?
Jul 01, 2025 am 01:27 AM
The following points should be noted when processing dates and time in JavaScript: 1. There are many ways to create Date objects. It is recommended to use ISO format strings to ensure compatibility; 2. Get and set time information can be obtained and set methods, and note that the month starts from 0; 3. Manually formatting dates requires strings, and third-party libraries can also be used; 4. It is recommended to use libraries that support time zones, such as Luxon. Mastering these key points can effectively avoid common mistakes.
 Why should you place tags at the bottom of the ?
Jul 02, 2025 am 01:22 AM
Why should you place tags at the bottom of the ?
Jul 02, 2025 am 01:22 AM
PlacingtagsatthebottomofablogpostorwebpageservespracticalpurposesforSEO,userexperience,anddesign.1.IthelpswithSEObyallowingsearchenginestoaccesskeyword-relevanttagswithoutclutteringthemaincontent.2.Itimprovesuserexperiencebykeepingthefocusonthearticl
 JavaScript vs. Java: A Comprehensive Comparison for Developers
Jun 20, 2025 am 12:21 AM
JavaScript vs. Java: A Comprehensive Comparison for Developers
Jun 20, 2025 am 12:21 AM
JavaScriptispreferredforwebdevelopment,whileJavaisbetterforlarge-scalebackendsystemsandAndroidapps.1)JavaScriptexcelsincreatinginteractivewebexperienceswithitsdynamicnatureandDOMmanipulation.2)Javaoffersstrongtypingandobject-orientedfeatures,idealfor
 JavaScript: Exploring Data Types for Efficient Coding
Jun 20, 2025 am 12:46 AM
JavaScript: Exploring Data Types for Efficient Coding
Jun 20, 2025 am 12:46 AM
JavaScripthassevenfundamentaldatatypes:number,string,boolean,undefined,null,object,andsymbol.1)Numbersuseadouble-precisionformat,usefulforwidevaluerangesbutbecautiouswithfloating-pointarithmetic.2)Stringsareimmutable,useefficientconcatenationmethodsf
 What is event bubbling and capturing in the DOM?
Jul 02, 2025 am 01:19 AM
What is event bubbling and capturing in the DOM?
Jul 02, 2025 am 01:19 AM
Event capture and bubble are two stages of event propagation in DOM. Capture is from the top layer to the target element, and bubble is from the target element to the top layer. 1. Event capture is implemented by setting the useCapture parameter of addEventListener to true; 2. Event bubble is the default behavior, useCapture is set to false or omitted; 3. Event propagation can be used to prevent event propagation; 4. Event bubbling supports event delegation to improve dynamic content processing efficiency; 5. Capture can be used to intercept events in advance, such as logging or error processing. Understanding these two phases helps to accurately control the timing and how JavaScript responds to user operations.
 What's the Difference Between Java and JavaScript?
Jun 17, 2025 am 09:17 AM
What's the Difference Between Java and JavaScript?
Jun 17, 2025 am 09:17 AM
Java and JavaScript are different programming languages. 1.Java is a statically typed and compiled language, suitable for enterprise applications and large systems. 2. JavaScript is a dynamic type and interpreted language, mainly used for web interaction and front-end development.






