To help you achieve your goals in 2025 as a Software Developer, I'm offering a complete Typescript course completely FREE!
? What will you learn?
? Class 001 - Primitive Types
? Class 002 - Objects and Arrays
? Class 003 - Functions
? Class 004 - Other types
? Class 005 - Union Types, Type Assertion and Literal Types
? Class 006 - Type Inference
? Class 007 - Interface and Types
? Class 008 - Generics
? Class 009 - Utility Types
? Class 010 - Classes (Part 1)
? Class 011 - Classes (Part 2)
? Class 012 - Extra Tips
? Class 013 - Practical challenge
You will learn everything that you will use most when working with Typescript in your daily life in a practical way.
If you already know Javascript, Typescript will be a game changer in your career, bringing more security and scalability to your code.
Setup
Before starting the class, we first need to configure the setup of our development environment, installing and configuring some tools that we will use.
Node Installation
If you don't have Node installed on your machine, you can go to https://nodejs.org/en/download and install it according to your operating system.
VS Code Installation
I will use VS Code as an editor, you can download it by going to https://code.visualstudio.com.
Typescript Installation
With Node installed, we can start the project and configure Typescript.
Create a folder and open the terminal in this newly created folder and run the following command by pressing ENTER:
npm init -y && code .
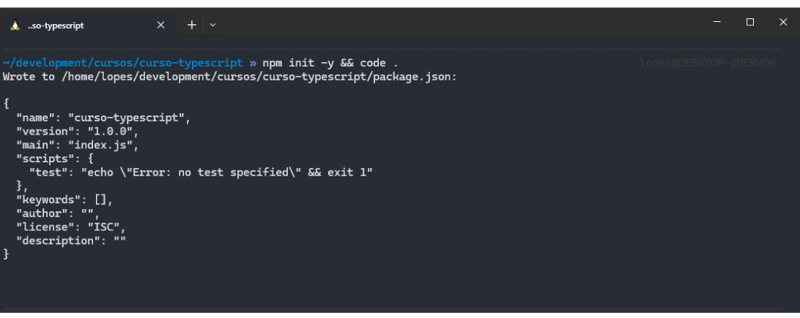
The command will create a package.json file and open VS Code in the folder. In VS Code click View > Terminal to open the integrated terminal.
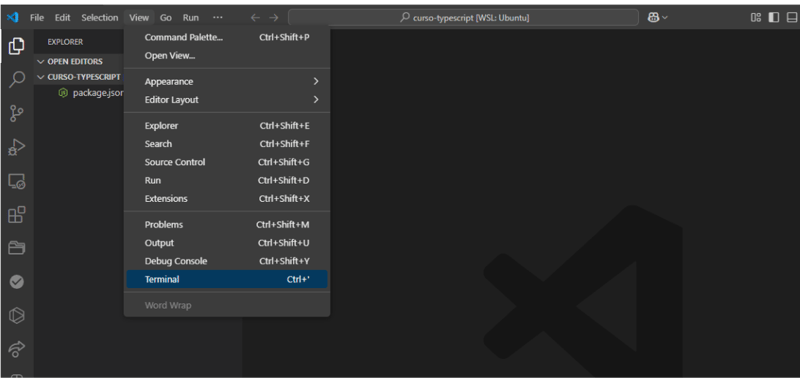
Now, in the integrated VS Code terminal, run the following command:
npm i -D typescript
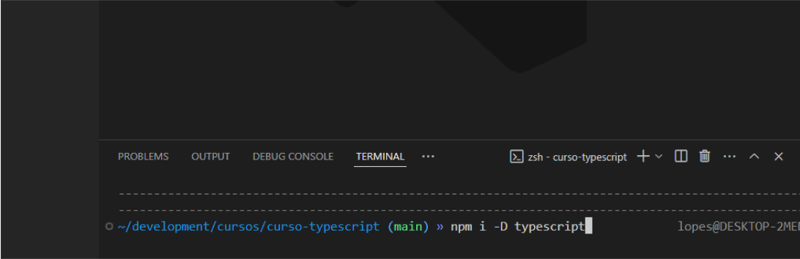
This command will install Typescript as a development dependency in our package.json.
Create a file called tsconfig.json and add the following configuration to the file:
{
"compilerOptions": {
"rootDir": "./src",
"outDir": "./dist",
"target": "ES2020",
"strict": true,
"noEmitOnError": true
}
}
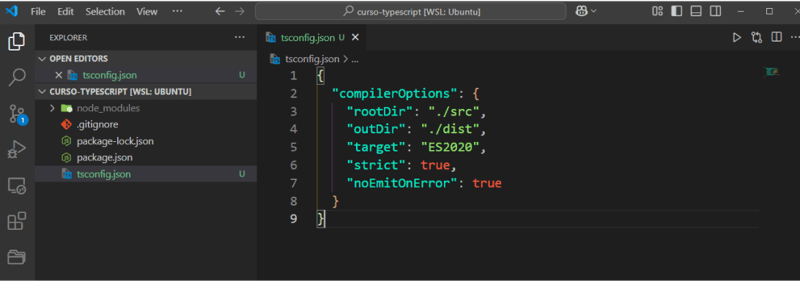
The tsconfig.json file is used to configure the Typescript compiler, there are several configurations that we can make, at this moment we are only interested in the following configurations:
- rootDir - Sets the path to Typescript files.
- outDir - Defines the output folder for Javascript files.
- target - Defines the version of Javascript that the compiler should use to compile the files.
- strict - Enables strict mode.
- noEmitOnError - Does not execute the compilation if there is any type of error.
You can find out about all the available options by visiting https://www.typescriptlang.org/docs/handbook/compiler-options.html
Access the package.json file and create a new build script with the command:
npm init -y && code .
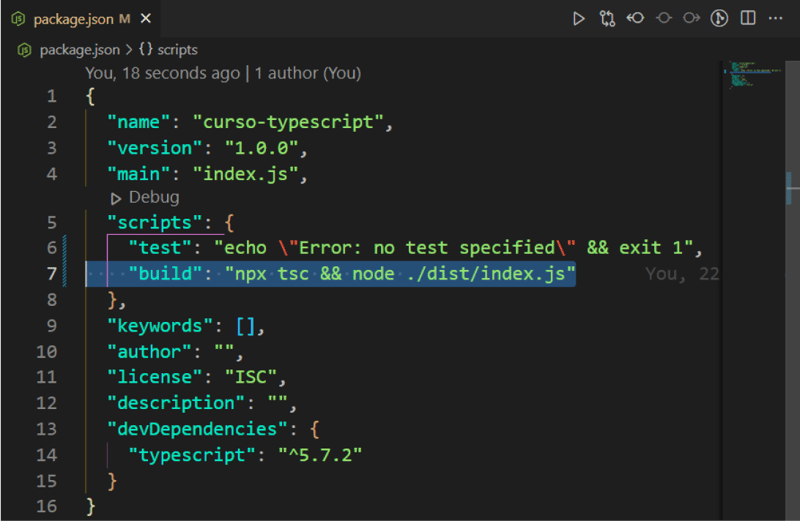
The browser, like Node, does not understand Typescript, we need to compile the Typescript code to Javascript so that it can understand and execute. This command will compile our Typescript code to Javascript so that we can run it in Node.
Remember, in the end all our Typescript code will become Javascript. Typescript is just a tool used in development to improve the type safety and scalability of our code.
To finish, create a folder called src and an index.ts file with the following code:
npm i -D typescript
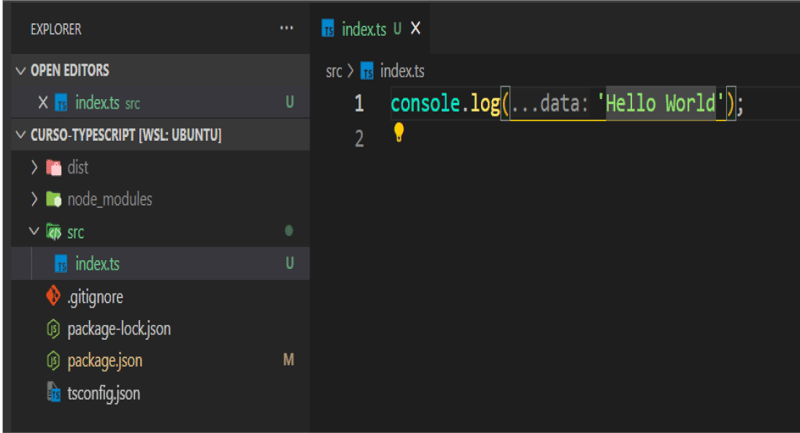
Now, let's test if everything works. Open the terminal and run:
{
"compilerOptions": {
"rootDir": "./src",
"outDir": "./dist",
"target": "ES2020",
"strict": true,
"noEmitOnError": true
}
}
When running, if everything is ok, you should see Hello World in the terminal.
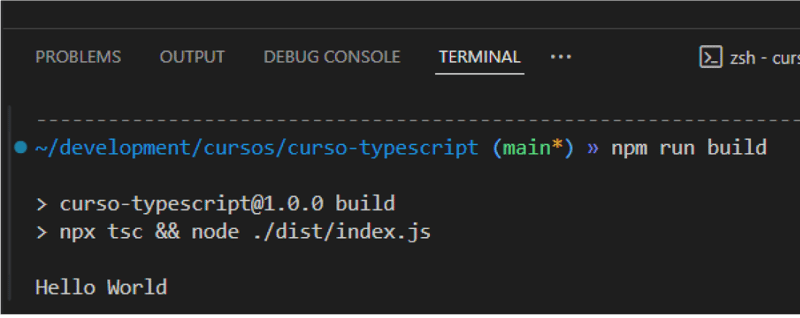
Whenever you want to see something in the console, you will need to run this command to compile the file to Javascript, okay?
Primitive types
In TypeScript, there are six primitive types which are: string, number, boolean, symbol, bigint, null and undefined.
npx tsc && node ./dist/index.js
String
A string is anything enclosed in quotation marks. It can be single quotes ('’), double quotes ("") or backquotes ().
number
There is no distinction here: integers, decimals, positives, negatives, everything is treated as a number.
Boolean
The true or false classic.
symbol
A bit abstract, but symbol is a unique identifier. Think of it as a fingerprint for objects.
Bigint
If a number is already big, bigint is almost infinite. Use it to deal with numbers that even a scientific calculator cannot solve.
Null
Represents a variable that has no value.
Undefined
Represents an uninitialized value.
You can access the class code by accessing the link below:
https://github.com/d3vlopes/curso-typescript/tree/aula-001
Next class
In the next class, we will learn about Objects and Arrays in Typescript.
? Questions or problems?
Did you have any problems with the setup configuration? Do you have any questions about the class? Post it here in the comments, let's together build quality material that is accessible to everyone.
The above is the detailed content of Free Typescript 5 Course. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 Java vs. JavaScript: Clearing Up the Confusion
Jun 20, 2025 am 12:27 AM
Java vs. JavaScript: Clearing Up the Confusion
Jun 20, 2025 am 12:27 AM
Java and JavaScript are different programming languages, each suitable for different application scenarios. Java is used for large enterprise and mobile application development, while JavaScript is mainly used for web page development.
 Javascript Comments: short explanation
Jun 19, 2025 am 12:40 AM
Javascript Comments: short explanation
Jun 19, 2025 am 12:40 AM
JavaScriptcommentsareessentialformaintaining,reading,andguidingcodeexecution.1)Single-linecommentsareusedforquickexplanations.2)Multi-linecommentsexplaincomplexlogicorprovidedetaileddocumentation.3)Inlinecommentsclarifyspecificpartsofcode.Bestpractic
 How to work with dates and times in js?
Jul 01, 2025 am 01:27 AM
How to work with dates and times in js?
Jul 01, 2025 am 01:27 AM
The following points should be noted when processing dates and time in JavaScript: 1. There are many ways to create Date objects. It is recommended to use ISO format strings to ensure compatibility; 2. Get and set time information can be obtained and set methods, and note that the month starts from 0; 3. Manually formatting dates requires strings, and third-party libraries can also be used; 4. It is recommended to use libraries that support time zones, such as Luxon. Mastering these key points can effectively avoid common mistakes.
 Why should you place tags at the bottom of the ?
Jul 02, 2025 am 01:22 AM
Why should you place tags at the bottom of the ?
Jul 02, 2025 am 01:22 AM
PlacingtagsatthebottomofablogpostorwebpageservespracticalpurposesforSEO,userexperience,anddesign.1.IthelpswithSEObyallowingsearchenginestoaccesskeyword-relevanttagswithoutclutteringthemaincontent.2.Itimprovesuserexperiencebykeepingthefocusonthearticl
 JavaScript vs. Java: A Comprehensive Comparison for Developers
Jun 20, 2025 am 12:21 AM
JavaScript vs. Java: A Comprehensive Comparison for Developers
Jun 20, 2025 am 12:21 AM
JavaScriptispreferredforwebdevelopment,whileJavaisbetterforlarge-scalebackendsystemsandAndroidapps.1)JavaScriptexcelsincreatinginteractivewebexperienceswithitsdynamicnatureandDOMmanipulation.2)Javaoffersstrongtypingandobject-orientedfeatures,idealfor
 JavaScript: Exploring Data Types for Efficient Coding
Jun 20, 2025 am 12:46 AM
JavaScript: Exploring Data Types for Efficient Coding
Jun 20, 2025 am 12:46 AM
JavaScripthassevenfundamentaldatatypes:number,string,boolean,undefined,null,object,andsymbol.1)Numbersuseadouble-precisionformat,usefulforwidevaluerangesbutbecautiouswithfloating-pointarithmetic.2)Stringsareimmutable,useefficientconcatenationmethodsf
 What is event bubbling and capturing in the DOM?
Jul 02, 2025 am 01:19 AM
What is event bubbling and capturing in the DOM?
Jul 02, 2025 am 01:19 AM
Event capture and bubble are two stages of event propagation in DOM. Capture is from the top layer to the target element, and bubble is from the target element to the top layer. 1. Event capture is implemented by setting the useCapture parameter of addEventListener to true; 2. Event bubble is the default behavior, useCapture is set to false or omitted; 3. Event propagation can be used to prevent event propagation; 4. Event bubbling supports event delegation to improve dynamic content processing efficiency; 5. Capture can be used to intercept events in advance, such as logging or error processing. Understanding these two phases helps to accurately control the timing and how JavaScript responds to user operations.
 How can you reduce the payload size of a JavaScript application?
Jun 26, 2025 am 12:54 AM
How can you reduce the payload size of a JavaScript application?
Jun 26, 2025 am 12:54 AM
If JavaScript applications load slowly and have poor performance, the problem is that the payload is too large. Solutions include: 1. Use code splitting (CodeSplitting), split the large bundle into multiple small files through React.lazy() or build tools, and load it as needed to reduce the first download; 2. Remove unused code (TreeShaking), use the ES6 module mechanism to clear "dead code" to ensure that the introduced libraries support this feature; 3. Compress and merge resource files, enable Gzip/Brotli and Terser to compress JS, reasonably merge files and optimize static resources; 4. Replace heavy-duty dependencies and choose lightweight libraries such as day.js and fetch






