WordPress Markdown: A Comprehensive Guide to Plugins and Best Practices
Markdown simplifies web content creation, but WordPress lacks native support. This guide explores efficient methods for using Markdown in WordPress, focusing on top-performing plugins and addressing common pitfalls. We'll also highlight plugins to avoid.
Key Considerations:
- Conversion or Plugins: You can either convert Markdown to HTML manually before pasting into WordPress or utilize a dedicated plugin.
- Plugin Conflicts: Avoid using multiple Markdown plugins simultaneously to prevent formatting inconsistencies.
- Editor Choice: Using the text editor instead of the visual editor minimizes unexpected formatting issues.
Top 5 WordPress Markdown Plugins (Actively Maintained):
-
WP Githuber MD: A comprehensive solution using GitHub Flavored Markdown. Features include syntax highlighting, live preview, spell check, image pasting, HTML-to-Markdown conversion, and per-post Markdown enabling/disabling. It's highly rated and actively developed, making it a top recommendation. Note: manual list continuation is required (new number/hyphen/asterisk per line).

-
Jetpack: A versatile plugin offering various features, including Markdown support (CommonMark syntax). Markdown editing requires manual activation within Jetpack settings. LaTeX support is available for mathematical expressions. While it lacks syntax highlighting and a preview pane, it reliably saves Markdown for future editing and automatically converts to HTML upon publishing.

-
WP Editor.md: This plugin provides syntax highlighting and a preview pane, though documentation is limited. Its interface resembles WP Githuber MD, utilizing Jetpack's Markdown module for parsing and saving. Note: potential double-spacing of lists in the preview, but correct rendering upon publishing. Conversion to HTML is permanent.

-
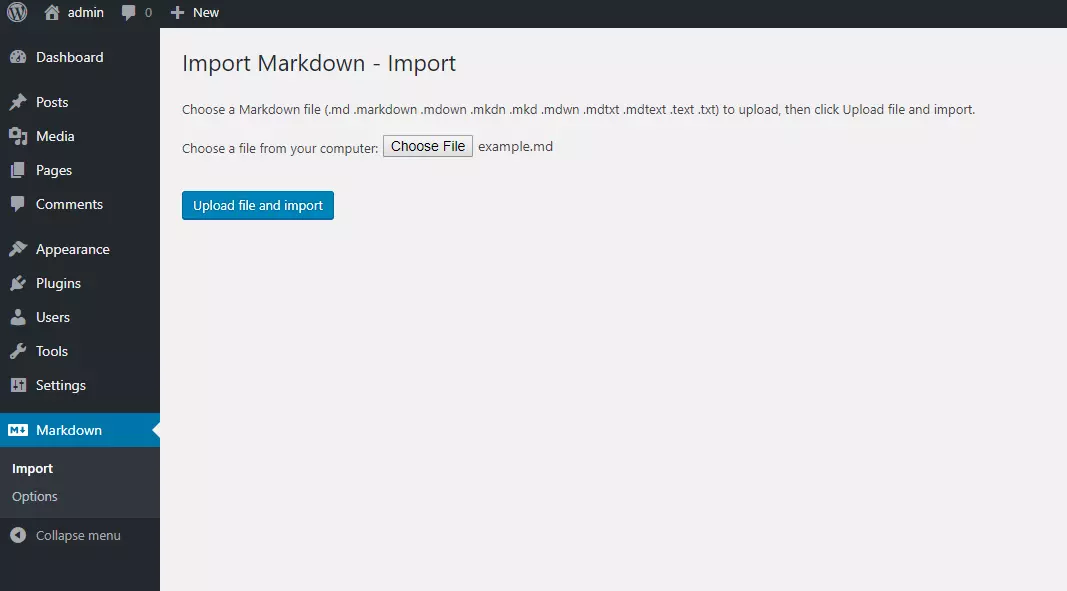
Import Markdown: This plugin isn't an editor but efficiently imports externally created Markdown files, supporting various Markdown flavors through selectable parsers.

-
Iceberg: A premium ($49) plugin offering a streamlined writing experience within the WordPress block editor, prioritizing writing flow over block manipulation. Popular among SitePoint editors for its intuitive design.

Plugins to Avoid (Outdated or Problematic):
Several older plugins are no longer maintained and may cause compatibility issues: PrettyPress, Typewriter, Markdown QuickTags, Easy Markdown. WP-Markdown, while actively developed, is a commercial plugin with a limited free version and overwhelmingly negative reviews for its paid offering.

Choosing the Right Plugin:
For dedicated Markdown functionality, WP Githuber MD is the recommended choice due to its feature richness, active development, and high ratings. Jetpack is a viable alternative if you need broader functionality beyond Markdown. Iceberg provides a premium, user-friendly experience within the block editor.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs):
The FAQs section from the original text is retained, ensuring comprehensive coverage of common user queries regarding Markdown plugins for WordPress.
The above is the detailed content of The Best Markdown Plugins for WordPress. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 How to use Git with WordPress
Jun 26, 2025 am 12:23 AM
How to use Git with WordPress
Jun 26, 2025 am 12:23 AM
When managing WordPress projects with Git, you should only include themes, custom plugins, and configuration files in version control; set up .gitignore files to ignore upload directories, caches, and sensitive configurations; use webhooks or CI tools to achieve automatic deployment and pay attention to database processing; use two-branch policies (main/develop) for collaborative development. Doing so can avoid conflicts, ensure security, and improve collaboration and deployment efficiency.
 How to use the WordPress testing environment
Jun 24, 2025 pm 05:13 PM
How to use the WordPress testing environment
Jun 24, 2025 pm 05:13 PM
Use WordPress testing environments to ensure the security and compatibility of new features, plug-ins or themes before they are officially launched, and avoid affecting real websites. The steps to build a test environment include: downloading and installing local server software (such as LocalWP, XAMPP), creating a site, setting up a database and administrator account, installing themes and plug-ins for testing; the method of copying a formal website to a test environment is to export the site through the plug-in, import the test environment and replace the domain name; when using it, you should pay attention to not using real user data, regularly cleaning useless data, backing up the test status, resetting the environment in time, and unifying the team configuration to reduce differences.
 How to create a simple Gutenberg block
Jun 28, 2025 am 12:13 AM
How to create a simple Gutenberg block
Jun 28, 2025 am 12:13 AM
The key to creating a Gutenberg block is to understand its basic structure and correctly connect front and back end resources. 1. Prepare the development environment: install local WordPress, Node.js and @wordpress/scripts; 2. Use PHP to register blocks and define the editing and display logic of blocks with JavaScript; 3. Build JS files through npm to make changes take effect; 4. Check whether the path and icons are correct when encountering problems or use real-time listening to build to avoid repeated manual compilation. Following these steps, a simple Gutenberg block can be implemented step by step.
 How to flush rewrite rules programmatically
Jun 27, 2025 am 12:21 AM
How to flush rewrite rules programmatically
Jun 27, 2025 am 12:21 AM
In WordPress, when adding a custom article type or modifying the fixed link structure, you need to manually refresh the rewrite rules. At this time, you can call the flush_rewrite_rules() function through the code to implement it. 1. This function can be added to the theme or plug-in activation hook to automatically refresh; 2. Execute only once when necessary, such as adding CPT, taxonomy or modifying the link structure; 3. Avoid frequent calls to avoid affecting performance; 4. In a multi-site environment, refresh each site separately as appropriate; 5. Some hosting environments may restrict the storage of rules. In addition, clicking Save to access the "Settings>Pinned Links" page can also trigger refresh, suitable for non-automated scenarios.
 How to set up redirects in WordPress htaccess
Jun 25, 2025 am 12:19 AM
How to set up redirects in WordPress htaccess
Jun 25, 2025 am 12:19 AM
TosetupredirectsinWordPressusingthe.htaccessfile,locatethefileinyoursite’srootdirectoryandaddredirectrulesabovethe#BEGINWordPresssection.Forbasic301redirects,usetheformatRedirect301/old-pagehttps://example.com/new-page.Forpattern-basedredirects,enabl
 How to make a WordPress theme responsive
Jun 28, 2025 am 12:14 AM
How to make a WordPress theme responsive
Jun 28, 2025 am 12:14 AM
To implement responsive WordPress theme design, first, use HTML5 and mobile-first Meta tags, add viewport settings in header.php to ensure that the mobile terminal is displayed correctly, and organize the layout with HTML5 structure tags; second, use CSS media query to achieve style adaptation under different screen widths, write styles according to the mobile-first principle, and commonly used breakpoints include 480px, 768px and 1024px; third, elastically process pictures and layouts, set max-width:100% for the picture and use Flexbox or Grid layout instead of fixed width; finally, fully test through browser developer tools and real devices, optimize loading performance, and ensure response
 How to send email from WordPress using SMTP
Jun 27, 2025 am 12:30 AM
How to send email from WordPress using SMTP
Jun 27, 2025 am 12:30 AM
UsingSMTPforWordPressemailsimprovesdeliverabilityandreliabilitycomparedtothedefaultPHPmail()function.1.SMTPauthenticateswithyouremailserver,reducingspamplacement.2.SomehostsdisablePHPmail(),makingSMTPnecessary.3.SetupiseasywithpluginslikeWPMailSMTPby
 How to integrate third-party APIs with WordPress
Jun 29, 2025 am 12:03 AM
How to integrate third-party APIs with WordPress
Jun 29, 2025 am 12:03 AM
Tointegratethird-partyAPIsintoWordPress,followthesesteps:1.SelectasuitableAPIandobtaincredentialslikeAPIkeysorOAuthtokensbyregisteringandkeepingthemsecure.2.Choosebetweenpluginsforsimplicityorcustomcodeusingfunctionslikewp_remote_get()forflexibility.