Excel date functions - formula examples of DATE, TODAY, etc.
May 07, 2025 am 09:03 AMThis is the final part of our Excel Date Tutorial that offers an overview of all Excel date functions, explains their basic uses and provides lots of formula examples.
Microsoft Excel provides a ton of functions to work with dates and times. Each function performs a simple operation and by combining several functions within one formula you can solve more complex and challenging tasks.
In the previous 12 parts of our Excel dates tutorial, we have studied the main Excel date functions in detail. In this final part, we are going to summarize the gained knowledge and provide links to a variety the formula examples to help you find the function best suited for calculating your dates.
The main function to calculate dates in Excel:
- DATE function
Get current date and time:
- TODAY - returns today's date
- NOW - returns the current date and time
Convert dates to / from text:
- DATEVALUE - converts a date in the text format to date format
- TEXT - converts a date to a text value
Retrieve dates in Excel:
- DAY - returns the day of the month
- MONTH - returns the month of a specified date
- YEAR - returns the year of a specified date
- EOMONTH - returns the last day of the month
- WEEKDAY - returns the day of the week
- WEEKNUM - returns the week number of a date
Calculate date difference:
- DATEDIF - returns the difference between two dates
- EDATE - returns a date N months before or after the start date
- YEARFRAC - calculates the fraction of the year between 2 dates
Calculate workdays:
- WORKDAY - returns a date N working days in the future or in the past
- WORKDAY.INTL - returns a date N weekdays from the start date with custom weekends
- NETWORKDAYS - returns the number of workdays between two dates
- NETWORKDAYS.INTL - returns the number of workdays between two dates with custom weekends
Excel DATE function
DATE(year, month, day) returns a serial number of a date based on the year, month and day values that you specify.
When it comes to working with dates in Excel, DATE is the most essential function to understand. The point is that other Excel date functions not always can recognize dates entered in the text format. So, when performing date calculations in Excel, you'd better supply dates using the DATE function to ensure the correct results.
Here are a few Excel DATE formula examples:
=DATE(2015, 5, 20) - returns a serial number corresponding to 20-May-2015.
=DATE(YEAR(TODAY()), MONTH(TODAY()), 1) - returns the first day of the current year and month.
=DATE(2015, 5, 20)-5 - subtracts 5 days from May 20, 2015.

At first sight, the Excel DATE function looks very simple, however, it does have a number of specificities pointed out in the Excel DATE tutorial.
Below you will find a few more examples where the Excel DATE function is part of bigger formulas:
- Subtracting two dates in Excel
- Adding or subtracting days to a date
- Calculate the number of days in a month
Excel TODAY function
The TODAY() function returns today's date, exactly as its name suggests.
TODAY is arguably one of the easiest Excel functions to use because it has no arguments at all. Whenever you need to get today's date in Excel, enter the following formula is a cell:
=TODAY()
Apart from this obvious use, the Excel TODAY function can be part of more complex formulas and calculations based on today's date. For example, to add 7 days to the current date, enter the following formula in a cell:
=TODAY() 7
To add 30 weekdays to today's date excluding weekend days, use this one:
=WORKDAY(TODAY(), 30)

Note. The date returned by the TODAY function in Excel updates automatically when your worksheet is recalculated to reflect the current date.
For more formula examples demonstrating the use of the TODAY function in Excel, please check out the following tutorials:
- Excel TODAY function to insert today's date and more
- Convert today's date to text format
- Calculate weekdays based on today's date
- Find the 1st day of month based on today date
Excel NOW function
NOW() function returns the current date and time. As well as TODAY, it does not have any arguments. If you wish to display today's date and current time in your worksheet, simply put the following formula in a cell:
=NOW()
Note. As well as TODAY, Excel NOW is a volatile function that refreshes the returned value every time the worksheet is recalculated. Please note, the cell with the NOW() formula does not auto update in real-time, only when the workbook is reopened or the worksheet is recalculated. To force the spreadsheet to recalculate, and consequently get your NOW formula to update its value, press either Shift F9 to recalculate only the active worksheet or F9 to recalculate all open workbooks.
For more details, please see How to use NOW function in Excel.
Excel DATEVALUE function
DATEVALUE(date_text) converts a date in the text format to a serial number that represents a date.
The DATEVALUE function understands plenty of date formats as well as references to cells that contain "text dates". DATEVALUE comes in really handy to calculate, filter or sort dates stored as text and convert such "text dates" to the Date format.
A few simple DATEVALUE formula examples follow below:
=DATEVALUE("20-may-2015")
=DATEVALUE("5/20/2015")
=DATEVALUE("may 20, 2015")

And the following examples demonstrate how the DATEVALUE function can help with solving real-life tasks:
- DATEVALUE formula to convert a date to a number
- DATEVALUE formula to convert a text string to a date
Excel TEXT function
In the pure sense, the TEXT function cannot be classified as one of Excel date functions because it can convert any numeric value, not only dates, to a text string.
With the TEXT(value, format_text) function, you can change the dates to text strings in a variety of formats, as demonstrated in the following screenshot.

Note. Though the values returned by the TEXT function may look like usual Excel dates, they are text values in nature and therefore cannot be used in other formulas and calculations.
Here are a few more TEXT formula examples that you may find helpful:
- Excel TEXT function to convert date to text
- Converting a date to month and year
- Extract the month name from date
- Convert the month number to month name
Excel DAY function
DAY(serial_number) function returns a day of the month as an integer from 1 to 31.
Serial_number is the date corresponding to the day you are trying to get. It can be a cell reference, a date entered by using the DATE function, or returned by other formulas.
Here are a few formula examples:
=DAY(A2) - returns the day of the month from a date in A2
=DAY(DATE(2015,1,1)) - returns the day of 1-Jan-2015
=DAY(TODAY()) - returns the day of today's date

Excel MONTH function
MONTH(serial_number) function in Excel returns the month of a specified date as an integer ranging from 1 (January) to 12 (December).
For example:
=MONTH(A2) - returns the month of a date in cell A2.
=MONTH(TODAY()) - returns the current month.
The MONTH function is rarely used in Excel date formulas on its own. Most often you would utilize it in conjunction with other functions as demonstrated in the following examples:
- Add or subtract months to a date in Excel
- Calculating months between two dates
- Get a month from the week number
- Get a month number from a date in Excel
- Calculate the 1st day of a month
- Conditionally format dates based on month
For the detail explanation of the MONTH function's syntax and plenty more formula examples, please check out the following tutorial: Using the MONTH function in Excel.
Excel YEAR function
YEAR(serial_number) returns a year corresponding to a given date, as a number from 1900 to 9999.
The Excel YEAR function is very straightforward and you will hardly run into any difficulties when using it in your date calculations:
=YEAR(A2) - returns the year of a date in cell A2.
=YEAR("20-May-2015") - returns the year of the specified date.
=YEAR(DATE(2015,5,20)) - a more reliable method to get the year of a given date.
=YEAR(TODAY()) - returns the current year.

For more information about the YEAR function, please see:
- Excel YEAR function - syntax and uses
- How to convert date to year in Excel
- How to add or subtract years to date in Excel
- Calculating years between two dates
- How to get the day of year (1 - 365)
- How to find the number of days remaining in the year
Excel EOMONTH function
EOMONTH(start_date, months) function returns the last day of the month a given number of months from the start date.
Like most of Excel date functions, EOMONTH can operate on dates input as cell references, entered by using the DATE function, or results of other formulas.
A positive value in the months argument adds the corresponding number of months to the start date, for example:
=EOMONTH(A2, 3) - returns the last day of the month, 3 months after the date in cell A2.
A negative value in the months argument subtracts the corresponding number of months from the start date:
=EOMONTH(A2, -3) - returns the last day of the month, 3 months before the date in cell A2.
A zero in the months argument forces the EOMONTH function to return the last day of the start date's month:
=EOMONTH(DATE(2015,4,15), 0) - returns the last day in April, 2015.
To get the last day of the current month, enter the TODAY function in the start_date argument and 0 in months:
=EOMONTH(TODAY(), 0)

You can find a few more EOMONTH formula examples in the following articles:
- How to get the last day of month
- How to get the first day of month
- Calculating leap years in Excel
Excel WEEKDAY function
WEEKDAY(serial_number,[return_type]) function returns the day of the week corresponding to a date, as a number from 1 (Sunday) to 7 (Saturday).
- Serial_number can be a date, a reference to a cell containing a date, or a date returned by some other Excel function.
- Return_type (optional) - is a number that determines which day of the week shall be considered the first day.
You can find the complete list of available return types in the following tutorial: Day of the week function in Excel.
And here are a few WEEKEND formula examples:
=WEEKDAY(A2) - returns the day of the week corresponding to a date in cell A2; the 1st day of the week is Sunday (default).
=WEEKDAY(A2, 2) - returns the day of the week corresponding to a date in cell A2; the week begins on Monday.
=WEEKDAY(TODAY()) - returns a number corresponding to today's day of the week; the week begins on Sunday.

The WEEKDAY function can help you determine which dates in your Excel sheet are working days and which ones are weekend days, and also sort, filter or highlight workdays and weekends:
- How to get a weekday name from date
- Find and filter workdays and weekends
- Highlight weekdays and weekends in Excel
Excel DATEDIF function
DATEDIF(start_date, end_date, unit) function is specially designed to calculate the difference between two dates in days, months or years.
Which time interval to use for calculating the date difference depends on the letter you enter in the last argument:
=DATEDIF(A2, TODAY(), "d") - calculates the number of days between the date in A2 and today's date.
=DATEDIF(A2, A5, "m") - returns the number of complete months between the dates in A2 and B2.
=DATEDIF(A2, A5, "y") - returns the number of complete years between the dates in A2 and B2.

These are just the basic applications of the DATEDIF function and it is capable of much more, as demonstrated in the following examples:
- Excel DATEDIF function - syntax and uses
- Count days between two dates
- Calculate weeks between the dates
- Calculate months between two dates
- Compute years between two dates
- Date difference is days, months and years
Excel WEEKNUM function
WEEKNUM(serial_number, [return_type]) - returns the week number of a specific date as an integer from 1 to 53.
For example, the below formula returns 1 because the week containing January 1 is the first week in the year.
=WEEKNUM("1-Jan-2015")
The following tutorial explains all the specificities on the Excel WEEKNUM function: WEEKNUM function - calculating week number in Excel.
Alternatively you can skip directly to one of the formula examples:
- How to sum values by week number
- How to highlight cells based on the week number
Excel EDATE function
EDATE(start_date, months) function returns the serial number of the date that is the specified number of months before or after the start date.
For example:
=EDATE(A2, 5) - adds 5 months to the date in cell A2.
=EDATE(TODAY(), -5) - subtracts 5 months from today's date.
For a detailed explanation of EDATE formulas illustrated with formula examples, please see: How to use EDATE function in Excel.
Excel YEARFRAC function
YEARFRAC(start_date, end_date, [basis]) function calculates the proportion of the year between 2 dates.
This very specific function can be used to solve practical tasks such as calculating age from date of birth.
Excel WORKDAY function
WORKDAY(start_date, days, [holidays]) function returns a date N workdays before or after the start date. It automatically excludes weekend days from calculations as well as any holidays that you specify.
This function is very helpful for calculating milestones and other important events based on the standard working calendar.
For example, the following formula adds 45 weekdays to the start date in cell A2, ignoring holidays in cells B2:B8:
=WORKDAY(A2, 45, B2:B85)
For the detailed explanation of WORKDAY's syntax and more formula examples, please check out:
WORKDAY function - add or subtract workdays in Excel
Excel WORKDAY.INTL function
WORKDAY.INTL(start_date, days, [weekend], [holidays]) is a more powerful variation of the WORKDAY function introduced in Excel 2010.
WORKDAY.INTL allows calculating a date N number of workdays in the future or in the past with custom weekend parameters.
For example, to get a date 20 workdays after the start date in cell A2, with Monday and Sunday counted as weekend days, you can use either of the following formulas:
=WORKDAY.INTL(A2, 20, 2, 7)
or
=WORKDAY.INTL(A2, 20, "1000001")
Of course, it might be difficult to grasp the essence from this short explanation, but more formula examples illustrated with screenshots will make things really easy:
WORKDAY.INTL - calculating workdays with custom weekends
Excel NETWORKDAYS function
NETWORKDAYS(start_date, end_date, [holidays]) function returns the number of weekdays between two dates that you specify. It automatically excludes weekend days and, optionally, the holidays.
For example, the following formula calculates the number of whole workdays between the start date in A2 and end date in B2, ignoring Saturdays and Sundays and excluding holidays in cells C2:C5:
=NETWORKDAYS(A2, B2, C2:C5)
You can find a comprehensive explanation of the NETWORKDAYS function's arguments illustrated with formula examples and screenshots in the following tutorial:
NETWORKDAYS function - calculating workdays between two dates
Excel NETWORKDAYS.INTL function
NETWORKDAYS.INTL(start_date, end_date, [weekend], [holidays]) is a more powerful modification of the NETWORKDAYS function available in Excel 2010 and later. It also returns the number of weekdays between two dates, but lets you specify which days should be counted as weekends.
Here is a basic NETWORKDAYS formula:
=NETWORKDAYS(A2, B2, 2, C2:C5)
The formula calculates the number of workdays between the date in A2 (start_date) and the date in B2 (end_date), excluding the weekend days Sunday and Monday (number 2 in the weekend parameter), and ignoring holidays in cells C2:C5.
For full details about the NETWORKDAYS.INTL function, please see:
NETWORKDAYS function - counting workdays with custom weekends
Hopefully, this 10K foot view on the Excel date functions has helped you gain the general understanding of how date formulas work in Excel. If you want to learn more, I encourage you to check out the formula examples referenced on this page. I thank you for reading and hope to see you again on our blog next week!
The above is the detailed content of Excel date functions - formula examples of DATE, TODAY, etc.. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 How to Use Parentheses, Square Brackets, and Curly Braces in Microsoft Excel
Jun 19, 2025 am 03:03 AM
How to Use Parentheses, Square Brackets, and Curly Braces in Microsoft Excel
Jun 19, 2025 am 03:03 AM
Quick Links Parentheses: Controlling the Order of Opera
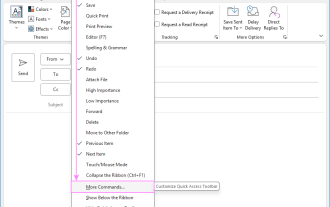 Outlook Quick Access Toolbar: customize, move, hide and show
Jun 18, 2025 am 11:01 AM
Outlook Quick Access Toolbar: customize, move, hide and show
Jun 18, 2025 am 11:01 AM
This guide will walk you through how to customize, move, hide, and show the Quick Access Toolbar, helping you shape your Outlook workspace to fit your daily routine and preferences. The Quick Access Toolbar in Microsoft Outlook is a usefu
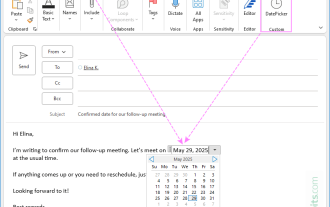 How to insert date picker in Outlook emails and templates
Jun 13, 2025 am 11:02 AM
How to insert date picker in Outlook emails and templates
Jun 13, 2025 am 11:02 AM
Want to insert dates quickly in Outlook? Whether you're composing a one-off email, meeting invite, or reusable template, this guide shows you how to add a clickable date picker that saves you time. Adding a calendar popup to Outlook email
 Prove Your Real-World Microsoft Excel Skills With the How-To Geek Test (Intermediate)
Jun 14, 2025 am 03:02 AM
Prove Your Real-World Microsoft Excel Skills With the How-To Geek Test (Intermediate)
Jun 14, 2025 am 03:02 AM
Whether you've secured a data-focused job promotion or recently picked up some new Microsoft Excel techniques, challenge yourself with the How-To Geek Intermediate Excel Test to evaluate your proficiency!This is the second in a three-part series. The
 How to Switch to Dark Mode in Microsoft Excel
Jun 13, 2025 am 03:04 AM
How to Switch to Dark Mode in Microsoft Excel
Jun 13, 2025 am 03:04 AM
More and more users are enabling dark mode on their devices, particularly in apps like Excel that feature a lot of white elements. If your eyes are sensitive to bright screens, you spend long hours working in Excel, or you often work after dark, swit
 How to Delete Rows from a Filtered Range Without Crashing Excel
Jun 14, 2025 am 12:53 AM
How to Delete Rows from a Filtered Range Without Crashing Excel
Jun 14, 2025 am 12:53 AM
Quick LinksWhy Deleting Filtered Rows Crashes ExcelSort the Data First to Prevent Excel From CrashingRemoving rows from a large filtered range in Microsoft Excel can be time-consuming, cause the program to temporarily become unresponsive, or even lea
 Microsoft Excel Essential Skills Test
Jun 12, 2025 pm 12:01 PM
Microsoft Excel Essential Skills Test
Jun 12, 2025 pm 12:01 PM
Whether you've landed a job interview for a role that requires basic Microsoft Excel skills or you're looking to solve a real-world problem, take the How-To Geek Beginner Excel Test to verify that you understand the fundamentals of this popular sprea
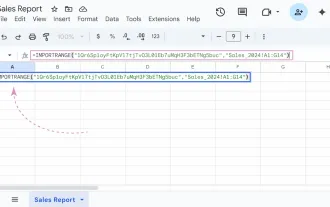 Google Sheets IMPORTRANGE: The Complete Guide
Jun 18, 2025 am 09:54 AM
Google Sheets IMPORTRANGE: The Complete Guide
Jun 18, 2025 am 09:54 AM
Ever played the "just one quick copy-paste" game with Google Sheets... and lost an hour of your life? What starts as a simple data transfer quickly snowballs into a nightmare when working with dynamic information. Those "quick fixes&qu






