To create a user-defined function in Excel VBA, you write a Function procedure in the Visual Basic Editor. 1. Open the VBA Editor by pressing Alt F11 and insert a standard module. 2. Write the Function Procedure starting with the Function keyword, defining arguments and their data types, and assigning the result to the function name, such as Function AddNumbers(a As Double, b As Double) As Double followed by AddNumbers = a b. 3. Use the function in Excel by typing =FunctionName(arguments) in a cell, ensuring the workbook is saved as .xlsm. 4. Optional: Add help descriptions via Tools → Macro → Options and include comments for clarity. Ensure functions are in standard modules and test them thoroughly for robustness.

To create a user-defined function in Excel VBA, you write a Function procedure in the Visual Basic Editor. This lets you build custom calculations that work like built-in Excel functions.

Open the VBA Editor and Insert a Module
Before writing your function, you need to access the VBA environment:

- Press
Alt F11to open the Visual Basic Editor. - In the Project window, right-click on any existing module (or your workbook name) → select Insert → choose Module.
This is where you’ll write your function code. Functions should be placed in standard modules for best results — not in sheet or workbook code areas.
Write the Function Procedure
A user-defined function starts with the Function keyword and ends with End Function. Here's a basic structure:

Function MyFunctionName(Argument1 As DataType, Argument2 As DataType) As ReturnType
' Your code here
End FunctionFor example, if you want a function that adds two numbers:
Function AddNumbers(a As Double, b As Double) As Double
AddNumbers = a b
End Function- The function name becomes the name you use in Excel formulas.
- Each argument should have a defined data type.
- The final result is assigned to the function name itself (
AddNumbers = ...).
You can now use =AddNumbers(2,3) in a worksheet cell just like any other formula.
Use the Function in Excel
Once written, your function appears in the formula bar when you start typing = in a cell. It won’t show up in the function list like built-in functions, but it will autocomplete once you know the name.
Some tips:
- Save your workbook as Excel Macro-Enabled Workbook (.xlsm) to keep the VBA code.
- If the function doesn’t appear, make sure it’s in a standard module and not inside a class or sheet module.
- You can add comments and error handling later to make it more robust.
Optional: Add Help and Descriptions
If you want others (or your future self) to understand what the function does without reading the code, you can add a description:
- In the VBA editor, go to Tools → Macro → Macros.
- Select your function → click Options → add a description.
This description shows up in the formula wizard under “Insert Function” in Excel.
Also, consider adding comments inside your function explaining what it does, especially if the logic gets complex.
That’s basically how you do it. Writing a UDF in VBA isn’t hard, but it’s powerful once you get the hang of it. Just remember to test your function with different inputs and handle possible errors, like text input when numbers are expected.
The above is the detailed content of how to create a user defined function in excel vba. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 How to Use Parentheses, Square Brackets, and Curly Braces in Microsoft Excel
Jun 19, 2025 am 03:03 AM
How to Use Parentheses, Square Brackets, and Curly Braces in Microsoft Excel
Jun 19, 2025 am 03:03 AM
Quick Links Parentheses: Controlling the Order of Opera
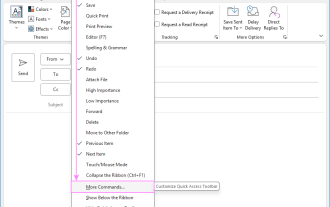 Outlook Quick Access Toolbar: customize, move, hide and show
Jun 18, 2025 am 11:01 AM
Outlook Quick Access Toolbar: customize, move, hide and show
Jun 18, 2025 am 11:01 AM
This guide will walk you through how to customize, move, hide, and show the Quick Access Toolbar, helping you shape your Outlook workspace to fit your daily routine and preferences. The Quick Access Toolbar in Microsoft Outlook is a usefu
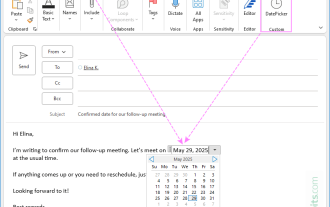 How to insert date picker in Outlook emails and templates
Jun 13, 2025 am 11:02 AM
How to insert date picker in Outlook emails and templates
Jun 13, 2025 am 11:02 AM
Want to insert dates quickly in Outlook? Whether you're composing a one-off email, meeting invite, or reusable template, this guide shows you how to add a clickable date picker that saves you time. Adding a calendar popup to Outlook email
 Prove Your Real-World Microsoft Excel Skills With the How-To Geek Test (Intermediate)
Jun 14, 2025 am 03:02 AM
Prove Your Real-World Microsoft Excel Skills With the How-To Geek Test (Intermediate)
Jun 14, 2025 am 03:02 AM
Whether you've secured a data-focused job promotion or recently picked up some new Microsoft Excel techniques, challenge yourself with the How-To Geek Intermediate Excel Test to evaluate your proficiency!This is the second in a three-part series. The
 How to Delete Rows from a Filtered Range Without Crashing Excel
Jun 14, 2025 am 12:53 AM
How to Delete Rows from a Filtered Range Without Crashing Excel
Jun 14, 2025 am 12:53 AM
Quick LinksWhy Deleting Filtered Rows Crashes ExcelSort the Data First to Prevent Excel From CrashingRemoving rows from a large filtered range in Microsoft Excel can be time-consuming, cause the program to temporarily become unresponsive, or even lea
 How to Switch to Dark Mode in Microsoft Excel
Jun 13, 2025 am 03:04 AM
How to Switch to Dark Mode in Microsoft Excel
Jun 13, 2025 am 03:04 AM
More and more users are enabling dark mode on their devices, particularly in apps like Excel that feature a lot of white elements. If your eyes are sensitive to bright screens, you spend long hours working in Excel, or you often work after dark, swit
 Microsoft Excel Essential Skills Test
Jun 12, 2025 pm 12:01 PM
Microsoft Excel Essential Skills Test
Jun 12, 2025 pm 12:01 PM
Whether you've landed a job interview for a role that requires basic Microsoft Excel skills or you're looking to solve a real-world problem, take the How-To Geek Beginner Excel Test to verify that you understand the fundamentals of this popular sprea
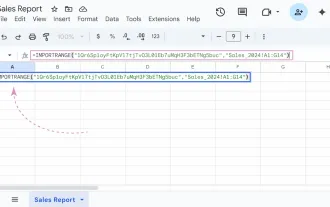 Google Sheets IMPORTRANGE: The Complete Guide
Jun 18, 2025 am 09:54 AM
Google Sheets IMPORTRANGE: The Complete Guide
Jun 18, 2025 am 09:54 AM
Ever played the "just one quick copy-paste" game with Google Sheets... and lost an hour of your life? What starts as a simple data transfer quickly snowballs into a nightmare when working with dynamic information. Those "quick fixes&qu






